Tutorial topic
The purpose of a tutorial is to show the reader how to “learn by doing” in a safe environment. A tutorial should build up easy successes. The length of a tutorial can vary from a few steps to many subtasks.
If you have an idea for a tutorial you’d like to develop, contact the Grafana Labs documentation team.
Internal contributors can reach out on Slack and external contributors can send email to docs@grafana.com or reach out on the #docs channel on the Grafana Labs Community Slack.
Tutorial structure
A tutorial topic includes the following elements:
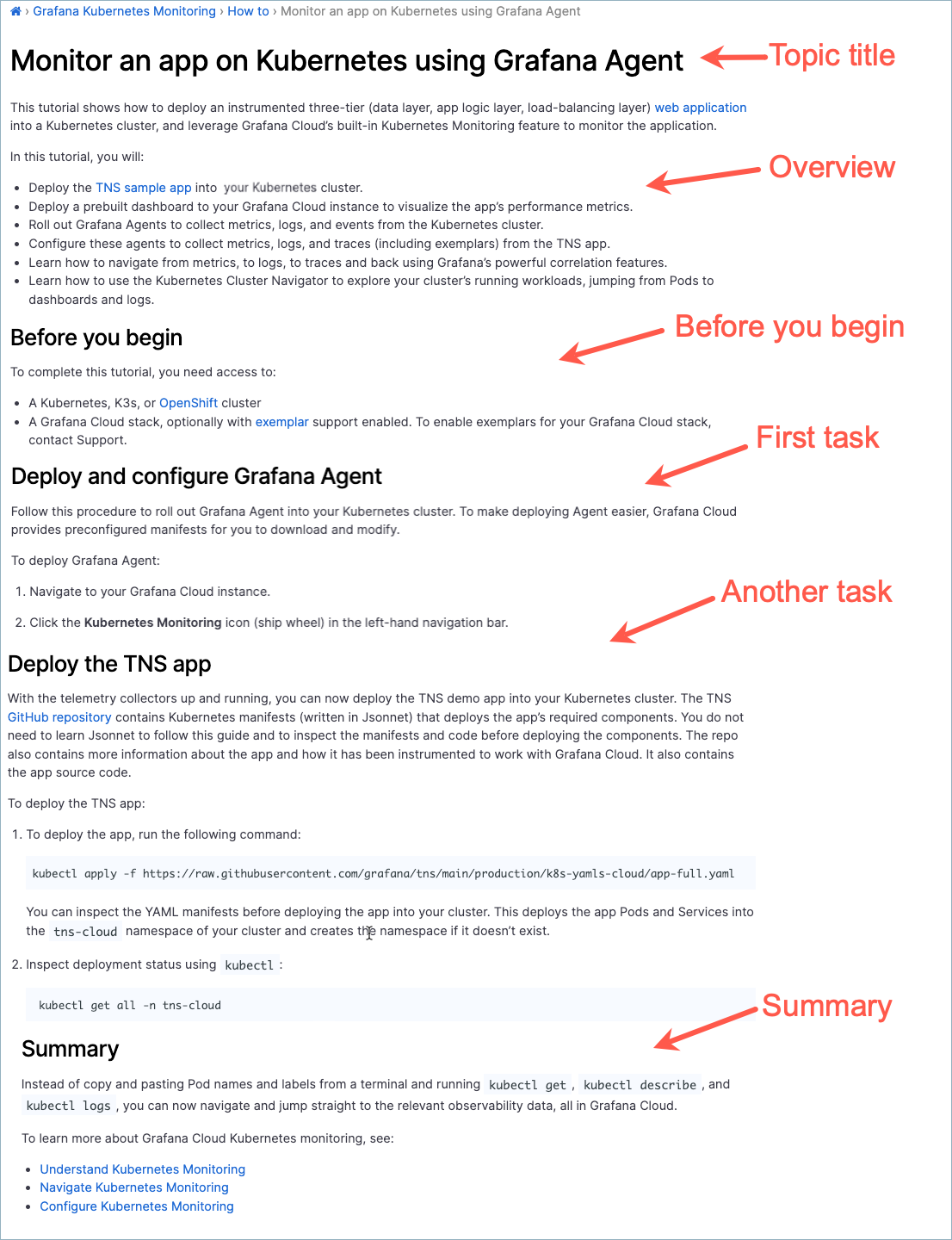
Topic title: Write a tutorial topic title that combines a verb and an object.
Overview: Let the user know the goal they will achieve by completing the tutorial. Provide context and include a list of the tasks the user will complete. Suggested text: “In this tutorial, you will …”.
There can be conceptual material in this section of a tutorial topic. However, limit conceptual information to only what’s relevant to the goal at hand.
If you find yourself writing a long introduction, consider creating a concept topic, and then writing a shorter form of that concept in the tutorial introduction. You can link to the concept topic from the tutorial.
Before you begin (optional): Describe or add links to tasks that a reader should complete before the tutorial. The links might sometimes be unrelated to the product, such as “Have this thing at hand.”
Additionally, this section can include decisions the user should make or permissions they need to confirm before starting the tutorial. Use a bulleted list if there is more than one prerequisite.
If there are no prerequisites, don’t include this section.
Task section (or sections): Create a section for each task needed to complete the tutorial. Follow the task guidelines to write the tasks.
To determine what tasks and steps you should include in your tutorial, perform a goal analysis and determine the valuable outcome the user wants to achieve. Limit the tutorial to the tasks needed to satisfy that goal. Work with a Subject Matter Expert (SME) to determine the goal and the minimal set of tasks. If possible, record the SME completing the tasks needed to accomplish the goal or ask the SME to record a demo of the tasks if that’s preferable.
Work with a Subject Matter Expert (SME) to:
- Provide steps that explain how to access or set up the data needed to complete the task. For more information, refer to Data for your tutorial.
- Don’t include written step numbers in the header, for example, “Step 1: Pick apples.”. Instead, include just the verb and object, for example “Pick apples.”
- Include only the tasks required for a straight path to the tutorial’s goal, not optional or alternative paths.
- Minimize the explanation within task steps. Instead, link to supporting explanations in related concept, task, and reference topics.
Summary (optional): Describe what the tutorial user has accomplished.
Next steps (optional): Provide logical next steps, if they exist.
Write a tutorial topic
To write a tutorial, complete these steps:
Add a
docs/sources/tutorialsdirectory to your project repository if one doesn’t yet exist.The tutorial is committed alongside the other documentation in your repository, and after it’s published, it’s displayed on the Grafana Tutorials page. For more information, refer to Publish your tutorial.
Create a child directory within the
tutorialsdirectory that follows this naming convention:- The directory name should include a verb and an object.
- Use lowercase letters.
- Add a hyphen between words.
Create an
index.mdfile within the tutorial’s directory.Add the content to a copy of the Tutorial template.
Add front matter to the
index.mdfile.For more information about front matter, refer to Front matter.
Tutorial template
When you are ready to write, make a copy of the Tutorial template and add your content.
Difference between tutorials and task topics
The difference between a tutorial and a task topic is that a tutorial is for learning, and a task is for actual operational work. Another important distinction is that a tutorial typically provides a “sandbox” environment—a source of data that users can safely experiment with.
Data for your tutorial
Depending on the application, your tutorial’s data might be:
- In a sandbox
- On test servers
- In demo repositories that the user clones locally
For example, the Play with Grafana Mimir tutorial provides a repository that users can clone to complete the tutorial. In contrast, the Store exemplars in Grafana Mimir topic is a pure task that a user would follow to complete their work. For guidance on writing tasks, refer to Tasks.
If getting access to the tutorial data is complex, include the instructions in the steps of the tutorial. If getting access to the data is straightforward, include it in the “Before you begin” section.
Publish your tutorial
You store your tutorial source in your project repository in a docs/sources/tutorials directory and mounted to the tutorials repository so that it’s displayed on the Tutorials page.
You store the source in your project repository to make it easy for team members to review and edit the content.
The following sections describe how to hide the tutorial from your project’s table of contents and to display it on the Tutorials page.
Hide your tutorial from your table of contents
Tutorials are for learning, so it’s best to keep them together on the Tutorials page, accessible directly from the Grafana website’s Learn menu. As such, you need to hide the tutorial so that it doesn’t appear in your project’s table of contents.
Before you begin
Before completing these steps, you need to create a tutorials directory under docs/sources and add your tutorial into its own subdirectory as described in the Write a tutorial topic section.
To hide your tutorial from your documentation’s table of contents:
Open your project’s
docs/sources/_index.mdfile.Add the following YAML to the page’s front matter, replacing
<PROJECT>with your project URL path.If the
cascadefront matter already exists, you must merge this snippet with the existing front matter.Note
Hugo
cascadefront matter can have two forms, array and mapping.The following snippet uses the array form of the
cascadefront matter. If your front matter isn’t already in the array form, you will need to change it to that form.For more information, refer to the
cascadefront matter documentationcascade: - _target: path: /docs/<PROJECT>/*/tutorials/** _build: list: false render: false
Add your tutorial to the Tutorials page
Note
This procedure is for writers who have permissions to update the Grafana website repository.
To add your tutorial to the Tutorials page:
Add the following YAML to the
manual_mountsfield in theconfig/_default/config.yamlfile in the website repository.Replace
<PROJECT>with your project name,<TUTORIAL>with the directory of your tutorial, and<VERSION>with the version of documentation you want to mount. Typically<VERSION>is either “next” or “latest”.- source: content/docs/<PROJECT>/<VERSION>/tutorials/<TUTORIAL> target: content/tutorials/k8s-monitoring-appAdd the following YAML to the
listfield in thedata/tutorials.yamlfile in the website repository.Replace
<TUTORIAL>with the directory of your tutorial and<LEVEL>with one of “beginner”, “intermediate”, or “advanced” depending on the difficulty of your tutorial.- page: /tutorials/<TUTORIAL> level: <LEVEL> type: tutorial
Tutorial topic examples
Refer to the following for tutorial examples:
