Warning
This plugin is now in maintenance mode, no new features will be added. We recommend using the Infinity data source plugin instead. If you want to get started quickly with CSV and Grafana, please read How to Visualize CSV Data with Grafana, which uses the recommended approach.
This page explains what each part of the query editor does, and how you can configure it.
The query editor for the CSV data source consists of a number of tabs. Each tab configures a part of the query.
Fields

The Fields tab is where you configure how to parse the data returned by the URL configured in the data source configuration.
- Delimiter defines how columns are separated in the file.
- Decimal separator defines the character used to separate the integer and fractional part of a number.
- Skip leading rows allows you to ignore a number of rows at the start of the data. This can be useful if your data contains comments, documentations, or other information before the data.
- Header tells Grafana whether the first row contains the names of each column.
- Ignore unknown toggles whether to display columns that aren’t defined in the schema. This can be useful if you’re only interested in a few columns.
By default, all columns in the CSV data are treated as text. If you want to parse a column into a specific type, such as Time or Number, you need to define a schema.
- Field references a column in the CSV data. If no header is present, you can reference the columns by their order, for example “Field 1”.
- Type defines the type of the column. If the type is anything other than String, the data source tries to parse the data into the specified type. Any values that can’t be parsed are ignored.
Path
The contents of this tab depends on whether the data source is set to HTTP or Local mode. In both cases, the path is relative to the data source URL.
HTTP
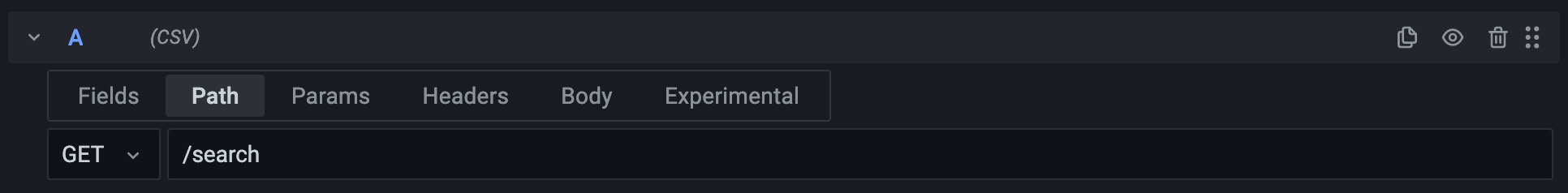
The drop-down box to the left lets you configure the HTTP method of the request sent to the URL and can be set to GET and POST.
The text box lets you append a path to the URL in the data source configuration. This can be used to dynamically change the request URL using variables.
For example, by setting the path to /movies/${movie}/summary you can query the summary for any movie without having to change the query itself.
Local
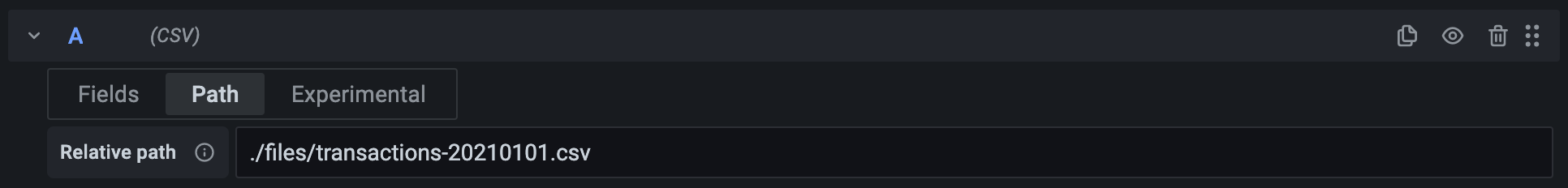
Relative path lets you append a relative path to the one in the data source configuration. For example, you can use the same data source to load multiple files by setting the Path in the data source configuration to a directory, and then use the Relative path to load a file within that directory.
Params
Only available in HTTP mode.
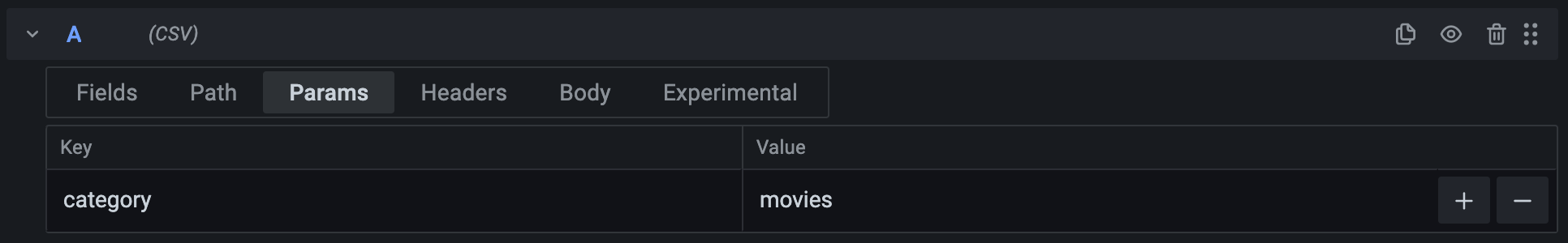
Add any parameters you’d like to send as part of the query string. For example, the parameters in the screenshot gets encoded as ?category=movies.
Both the Key and Value fields support variables.
:::caution Any query parameters that have been set by the administrator in the data source configuration has higher priority and overrides the parameters set by the query. :::
Headers
Only available in HTTP mode.
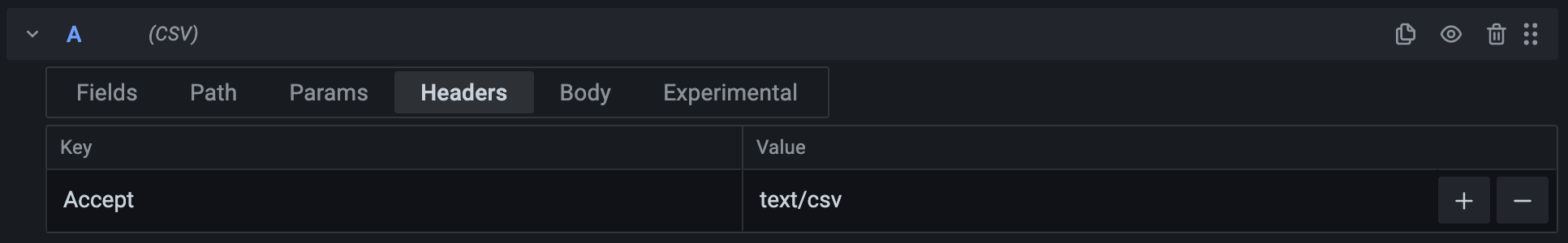
Add any parameters you’d like to send as HTTP headers.
Both the Key and Value fields support variables.
Body
Only available in HTTP mode.
Sets the text to send as a request body.
- Syntax highlighting sets the active syntax for the editor. This is only for visual purposes and doesn’t change the actual request.
:::info Due to limitations in modern browsers, Grafana ignores the request body if the HTTP method is set to GET. :::
Experimental
Try out features that are currently in development. Each feature has a link in its tooltip that takes you to the feature request on GitHub where you can share your feedback.
:::danger Experimental features might be unstable and can be removed without notice. :::
- Enable regular expressions lets you use regular expressions as field names in the schema. This lets you set the type for any field that matches the expression.



