Important: This documentation is about an older version. It's relevant only to the release noted, many of the features and functions have been updated or replaced. Please view the current version.
Google Cloud Monitoring data source
Grafana ships with built-in support for Google Cloud Monitoring. This topic describes queries, templates, variables, and other configuration specific to the Google Cloud Monitoring data source.
Note: Before Grafana v7.1, Google Cloud Monitoring was referred to as Google Stackdriver.
For instructions on how to add a data source to Grafana, refer to the administration documentation. Only users with the organization administrator role can add data sources.
Once you’ve added the Google Cloud Monitoring data source, you can configure it so that your Grafana instance’s users can create queries in its query editor and apply annotations when they build dashboards and use Explore.
Configure the data source
To access the data source configuration page:
- Hover the cursor over the Configuration (gear) icon.
- Select Data Sources.
- Select the Google Cloud Monitoring data source.
Set the data source’s basic configuration options carefully:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | Sets the name you use to refer to the data source in panels and queries. |
| Default | Sets whether the data source is pre-selected for new panels. |
Configure Google authentication
Before you can request data from Google Cloud Monitoring, you must configure authentication. All requests to Google APIs are performed on the server-side by the Grafana backend.
For authentication options and configuration details, refer to Google authentication.
When configuring Google authentication, note these additional Google Cloud Monitoring-specific steps:
Configure a GCP Service Account
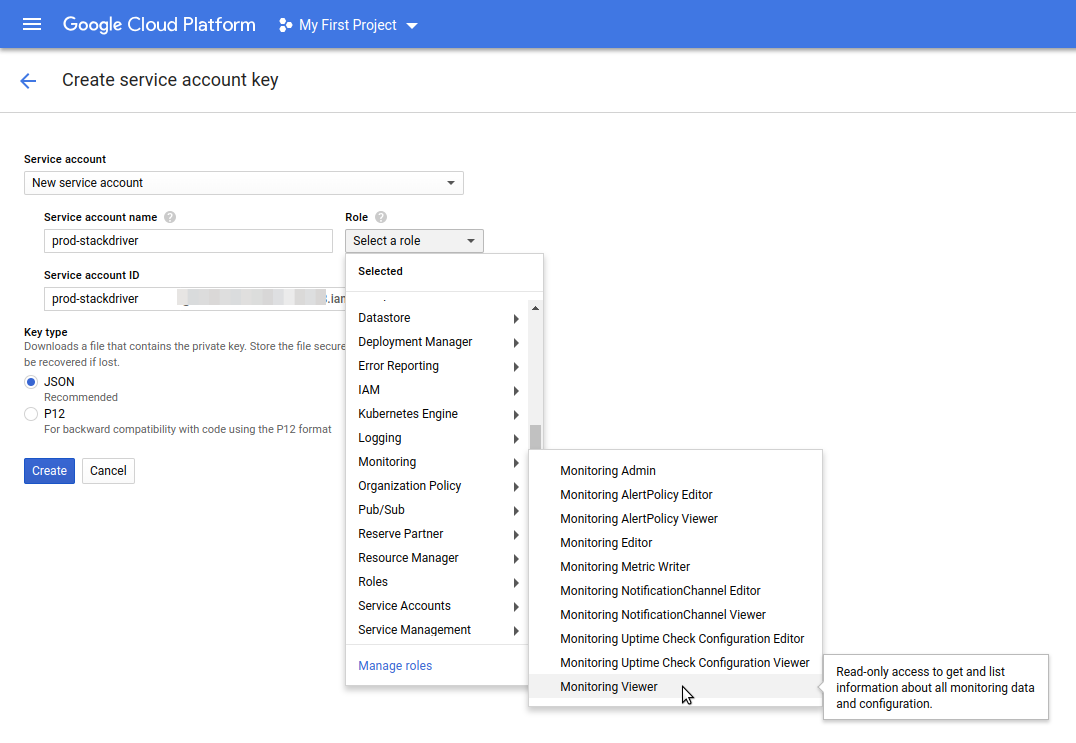
When you create a Google Cloud Platform (GCP) Service Account and key file, the Service Account must have the Monitoring Viewer role (Role > Select a role > Monitoring > Monitoring Viewer):
Grant the GCE Default Service Account scope
If Grafana is running on a Google Compute Engine (GCE) virtual machine, then when you Configure a GCE Default Service Account, you must also grant that Service Account access to the “Cloud Monitoring API” scope.
Enable necessary Google Cloud Platform APIs
Before you can request data from Google Cloud Monitoring, you must first enable necessary APIs on the Google end.
Open the Monitoring and Cloud Resource Manager API pages:
On each page, click the
Enablebutton.![Enable GCP APIs Enable GCP APIs]()
Enable GCP APIs
Provision the data source
You can define and configure the data source in YAML files as part of Grafana’s provisioning system. For more information about provisioning, and for available configuration options, refer to Provisioning Grafana.
Provisioning examples
Using the JWT (Service Account key file) authentication type:
apiVersion: 1
datasources:
- name: Google Cloud Monitoring
type: stackdriver
access: proxy
jsonData:
tokenUri: https://oauth2.googleapis.com/token
clientEmail: stackdriver@myproject.iam.gserviceaccount.com
authenticationType: jwt
defaultProject: my-project-name
secureJsonData:
privateKey: |
-----BEGIN PRIVATE KEY-----
POSEvQIBADANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQEFAASCBKcwggSjAgEAAoIBAQCb1u1Srw8ICYHS
...
yA+23427282348234=
-----END PRIVATE KEY-----Using GCE Default Service Account authentication:
apiVersion: 1
datasources:
- name: Google Cloud Monitoring
type: stackdriver
access: proxy
jsonData:
authenticationType: gceImport pre-configured dashboards
The Google Cloud Monitoring data source ships with pre-configured dashboards for some of the most popular GCP services. These curated dashboards are based on similar dashboards in the GCP dashboard samples repository.
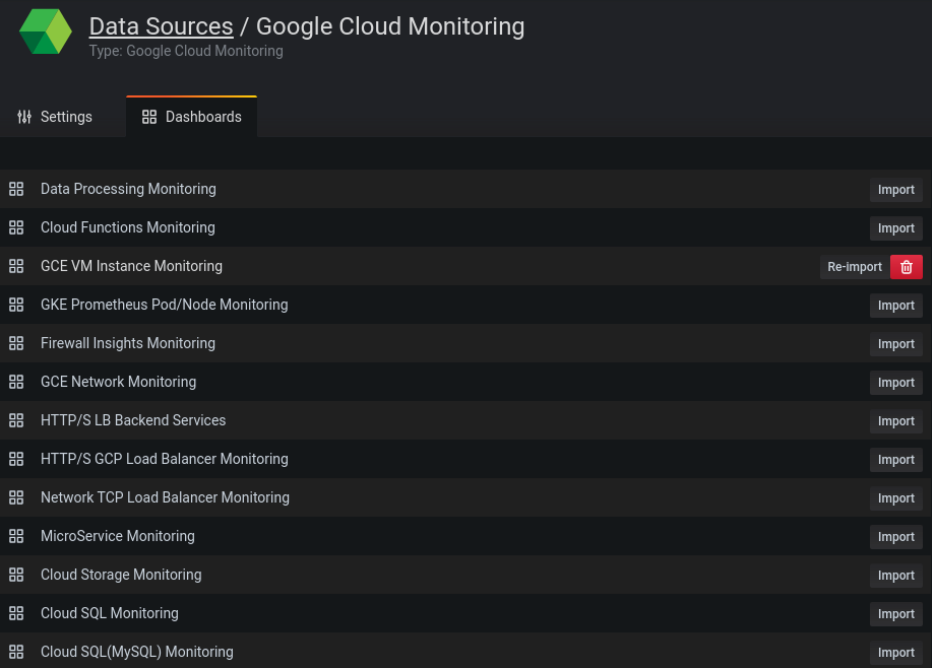
To import curated dashboards:
Navigate to the data source’s configuration page.
Select the Dashboards tab.
This displays the curated selection of importable dashboards.
Select Import for the dashboard to import.
The dashboards include a template variable populated with the projects accessible by the configured Service Account each time you load the dashboard. After Grafana loads the dashboard, you can select a project from the dropdown list.
To customize an imported dashboard:
To customize one of these dashboards, we recommend that you save it under a different name. If you don’t, upgrading Grafana can overwrite the customized dashboard with the new version.
Query the data source
The Google Cloud Monitoring query editor helps you build two types of queries: Metric and Service Level Objective (SLO).
For details, refer to the query editor documentation.
Use template variables
Instead of hard-coding details such as server, application, and sensor names in metric queries, you can use variables. Grafana lists these variables in dropdown select boxes at the top of the dashboard to help you change the data displayed in your dashboard. Grafana refers to such variables as template variables.
For details, see the template variables documentation.