Important: This documentation is about an older version. It's relevant only to the release noted, many of the features and functions have been updated or replaced. Please view the current version.
Using Graphite in Grafana
Grafana has an advanced Graphite query editor that lets you quickly navigate the metric space, add functions, change function parameters and much more. The editor can handle all types of graphite queries. It can even handle complex nested queries through the use of query references.
Adding the data source
- Open the side menu by clicking the Grafana icon in the top header.
- In the side menu under the
Configurationlink you should find a link namedData Sources. - Click the
+ Add data sourcebutton in the top header. - Select
Graphitefrom the Type dropdown.
NOTE: If you’re not seeing the
Data Sourceslink in your side menu it means that your current user does not have theAdminrole for the current organization.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | The data source name. This is how you refer to the data source in panels and queries. |
| Default | Default data source means that it will be pre-selected for new panels. |
| Url | The HTTP protocol, IP, and port of your graphite-web or graphite-api install. |
| Access | Server (default) = URL needs to be accessible from the Grafana backend/server, Browser = URL needs to be accessible from the browser. |
Access mode controls how requests to the data source will be handled. Server should be the preferred way if nothing else stated.
Server access mode (Default)
All requests will be made from the browser to Grafana backend/server which in turn will forward the requests to the data source and by that circumvent possible Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS) requirements. The URL needs to be accessible from the grafana backend/server if you select this access mode.
Browser access mode
All requests will be made from the browser directly to the data source and may be subject to Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS) requirements. The URL needs to be accessible from the browser if you select this access mode.
Metric editor
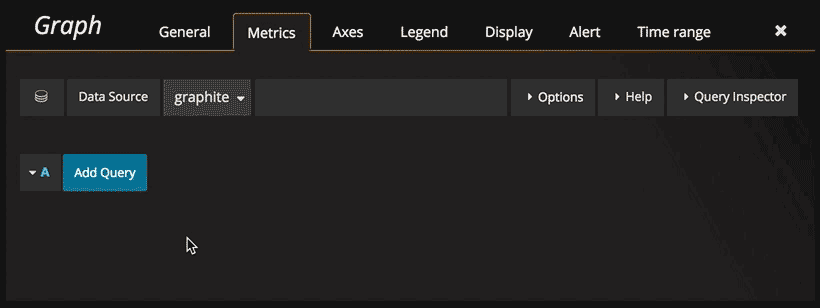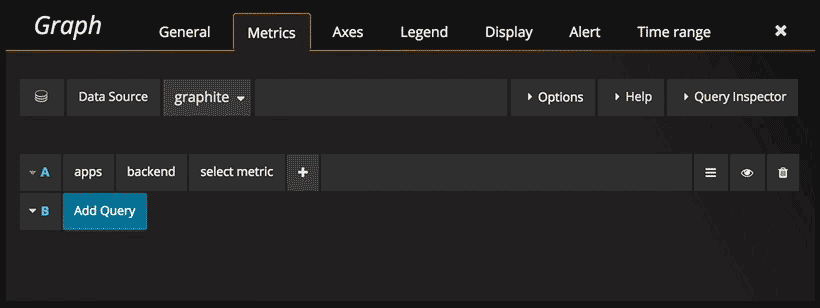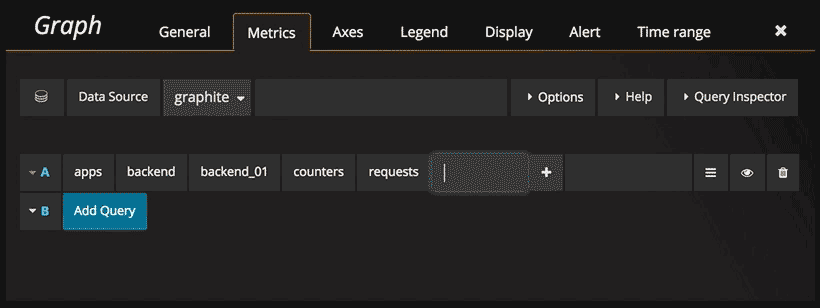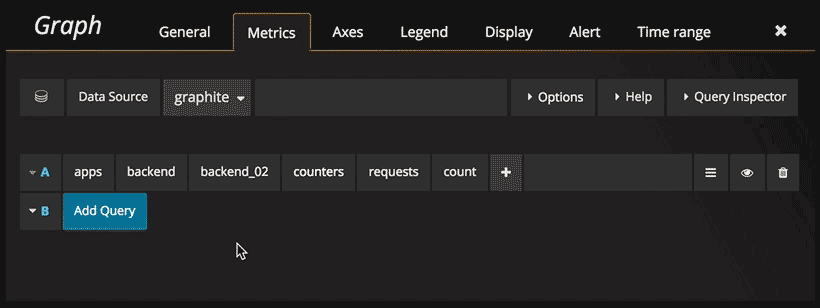
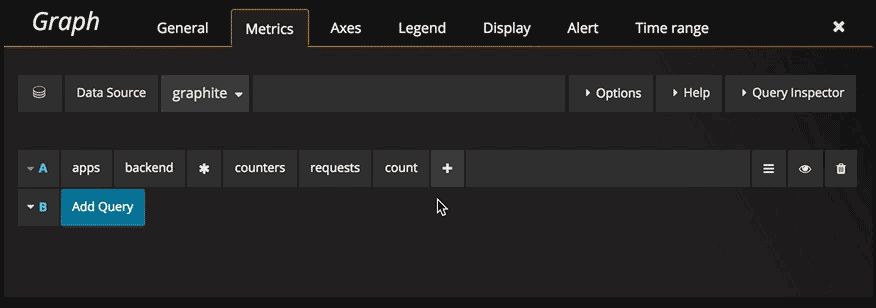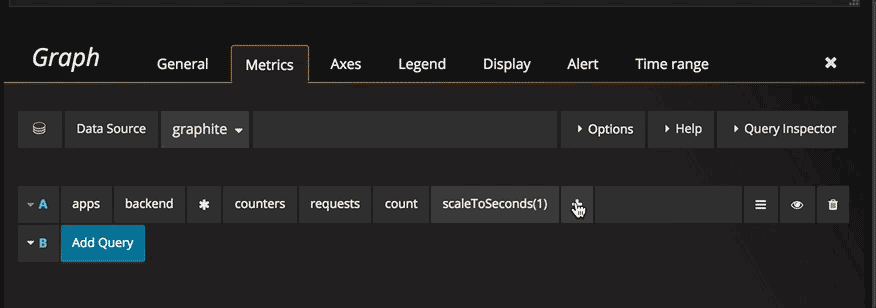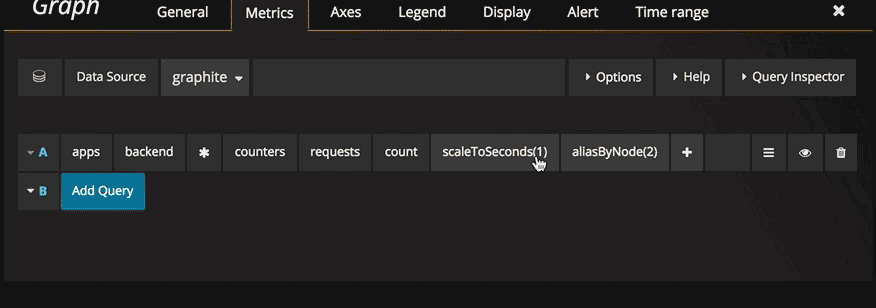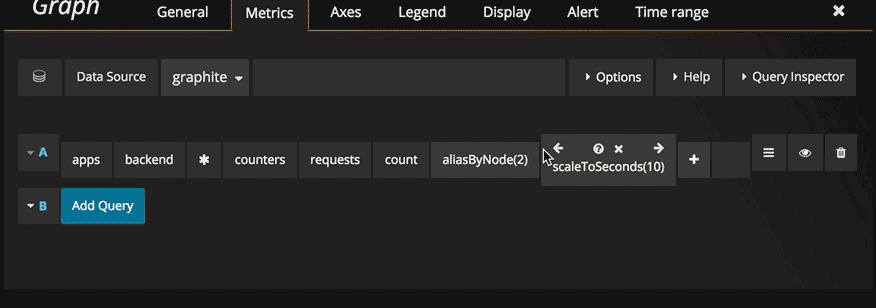
Navigate metric segments
Click the Select metric link to start navigating the metric space. Once you start you can continue using the mouse
or keyboard arrow keys. You can select a wildcard and still continue.
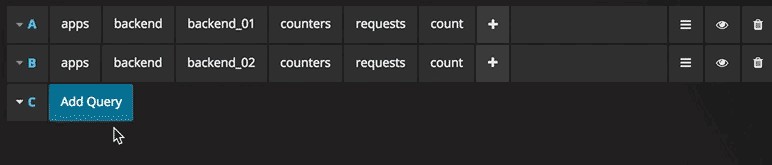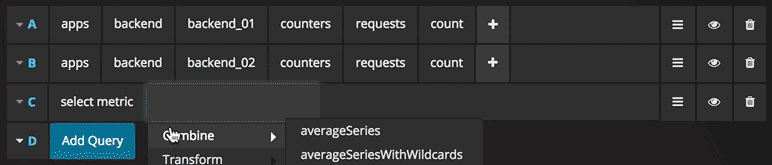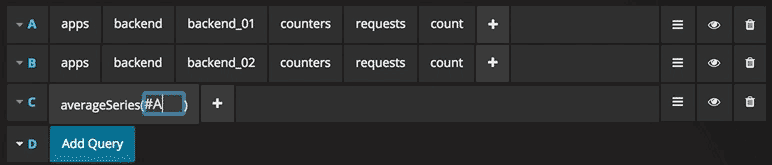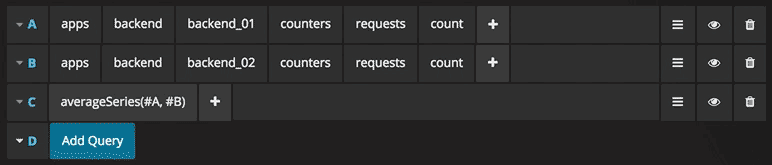
Functions
Click the plus icon to the right to add a function. You can search for the function or select it from the menu. Once a function is selected it will be added and your focus will be in the text box of the first parameter. To later change a parameter just click on it and it will turn into a text box. To delete a function click the function name followed by the x icon.
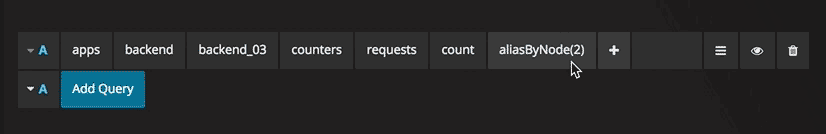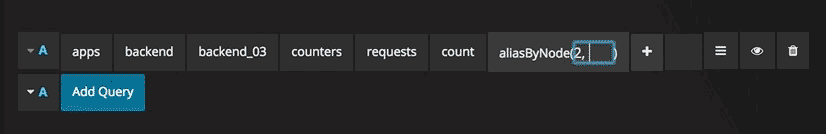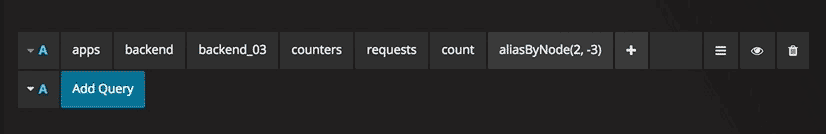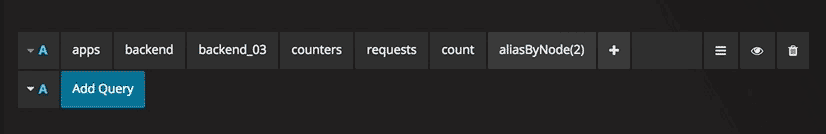
Optional parameters
Some functions like aliasByNode support an optional second argument. To add this parameter specify for example 3,-2 as the first parameter and the function editor will adapt and move the -2 to a second parameter. To remove the second optional parameter just click on it and leave it blank and the editor will remove it.
Nested Queries
You can reference queries by the row “letter” that they’re on (similar to Microsoft Excel). If you add a second query to a graph, you can reference the first query simply by typing in #A. This provides an easy and convenient way to build compounded queries.
Point consolidation
All Graphite metrics are consolidated so that Graphite doesn’t return more data points than there are pixels in the graph. By default,
this consolidation is done using avg function. You can control how Graphite consolidates metrics by adding the Graphite consolidateBy function.
Notice This means that legend summary values (max, min, total) cannot be all correct at the same time. They are calculated client side by Grafana. And depending on your consolidation function only one or two can be correct at the same time.
Templating
Instead of hard-coding things like server, application and sensor name in your metric queries you can use variables in their place. Variables are shown as dropdown select boxes at the top of the dashboard. These dropdowns make it easy to change the data being displayed in your dashboard.
Check out the Templating documentation for an introduction to the templating feature and the different types of template variables.
Graphite 1.1 introduced tags and Grafana added support for Graphite queries with tags in version 5.0. To create a variable using tag values, then you need to use the Grafana functions tags and tag_values.
| Query | Description |
|---|---|
| tags() | Returns all tags. |
| tags(server=~backend*) | Returns only tags that occur in series matching the filter expression. |
| tag_values(server) | Return tag values for the specified tag. |
| tag_values(server, server=~backend*) | Returns filtered tag values that occur for the specified tag in series matching those expressions. |
| tag_values(server, server=~backend*, app=~${apps:regex}) | Multiple filter expressions and expressions can contain other variables. |
For more details, see the Graphite docs on the autocomplete API for tags.
Query variable
The query you specify in the query field should be a metric find type of query. For example, a query like prod.servers.* will fill the
variable with all possible values that exist in the wildcard position.
You can also create nested variables that use other variables in their definition. For example
apps.$app.servers.* uses the variable $app in its query definition.
Using __searchFilter to filter results in Query Variable
Available from Grafana 6.5 and above
Using __searchFilter in the query field will filter the query result based on what the user types in the dropdown select box.
When nothing has been entered by the user the default value for __searchFilter is * and `` when used as part of a regular expression.
The example below shows how to use __searchFilter as part of the query field to enable searching for server while the user types in the dropdown select box.
Query
apps.$app.servers.$__searchFilterTagValues
tag_values(server, server=~${__searchFilter:regex})Variable Usage
You can use a variable in a metric node path or as a parameter to a function.

There are two syntaxes:
$<varname>Example: apps.frontend.$server.requests.count[[varname]]Example: apps.frontend.[[server]].requests.count
Why two ways? The first syntax is easier to read and write but does not allow you to use a variable in the middle of a word. Use
the second syntax in expressions like my.server[[serverNumber]].count.
Example: Graphite Templated Dashboard
Variable Usage in Tag Queries
Multi-value variables in tag queries use the advanced formatting syntax introduced in Grafana 5.0 for variables: {var:regex}. Non-tag queries will use the default glob formatting for multi-value variables.
Example of a tag expression with regex formatting and using the Equal Tilde operator, =~:
server=~${servers:regex}Check out the Advanced Formatting Options section in the Variables documentation for examples and details.
Annotations
Annotations allow you to overlay rich event information on top of graphs. You add annotation queries via the Dashboard menu / Annotations view.
Graphite supports two ways to query annotations. A regular metric query, for this you use the Graphite query textbox. A Graphite events query, use the Graphite event tags textbox,
specify a tag or wildcard (leave empty should also work)
Getting Grafana metrics into Graphite
Grafana exposes metrics for Graphite on the /metrics endpoint. For detailed instructions, refer to Internal Grafana metrics.
Configure the data source with provisioning
It’s now possible to configure data sources using config files with Grafana’s provisioning system. You can read more about how it works and all the settings you can set for data sources on the provisioning docs page
Here are some provisioning examples for this data source.
apiVersion: 1
datasources:
- name: Graphite
type: graphite
access: proxy
url: http://localhost:8080
jsonData:
graphiteVersion: "1.1"