Important: This documentation is about an older version. It's relevant only to the release noted, many of the features and functions have been updated or replaced. Please view the current version.
Histogram
Histograms calculate the distribution of values and present them as a bar chart. Each bar represents a bucket; the y-axis and the height of each bar represent the count of values that fall into each bucket, and the x-axis represents the value range.
For example, if you want to understand the distribution of people’s heights, you can use a histogram visualization to identify patterns or insights in the data distribution:
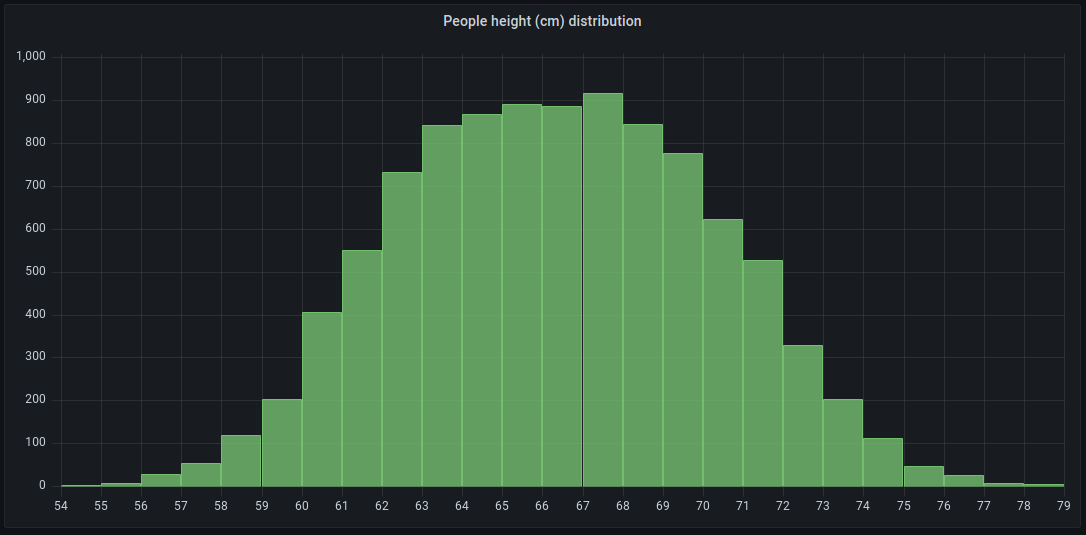
You can use a histogram visualization if you need to:
- Visualize and analyze data distributions over a specific time range to see how frequently certain values occur.
- Identify any outliers in your data distribution.
- Provide statistical analysis to help with decision-making
Configure a histogram visualization
Once you’ve created a dashboard, the following video shows you how to configure a histogram visualization:
With Grafana Play, you can explore and see how it works, learning from practical examples to accelerate your development. This feature can be seen on Histogram Examples.
Supported data formats
Histograms support time series and any table results with one or more numerical fields.
Examples
The following tables are examples of the type of data you need for a histogram visualization and how it should be formatted.
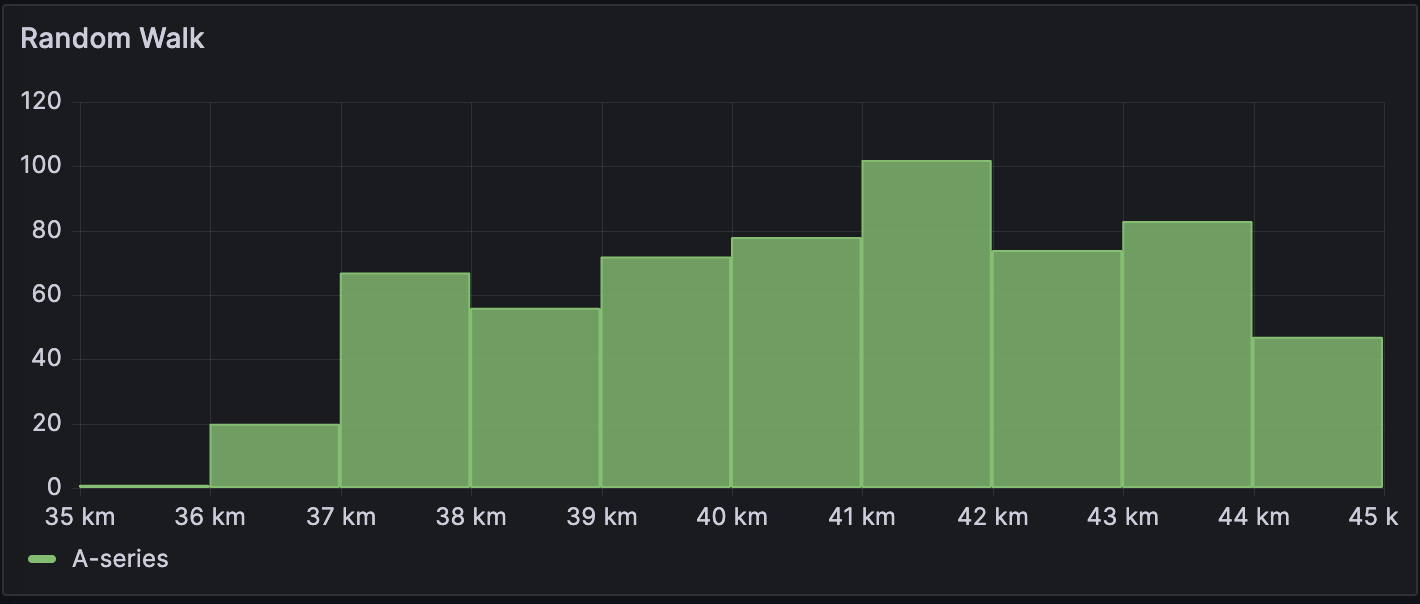
Time-series table
| Time | Walking (km) |
|---|---|
| 2024-03-25 21:13:09 | 37.2 |
| 2024-03-25 21:13:10 | 37.1 |
| 2024-03-25 21:13:10 | 37.0 |
| 2024-03-25 21:13:11 | 37.2 |
| 2024-03-25 21:13:11 | 36.9 |
| 2024-03-25 21:13:12 | 36.7 |
| 2024-03-25 21:13:13 | 36.3 |
The data is converted as follows:
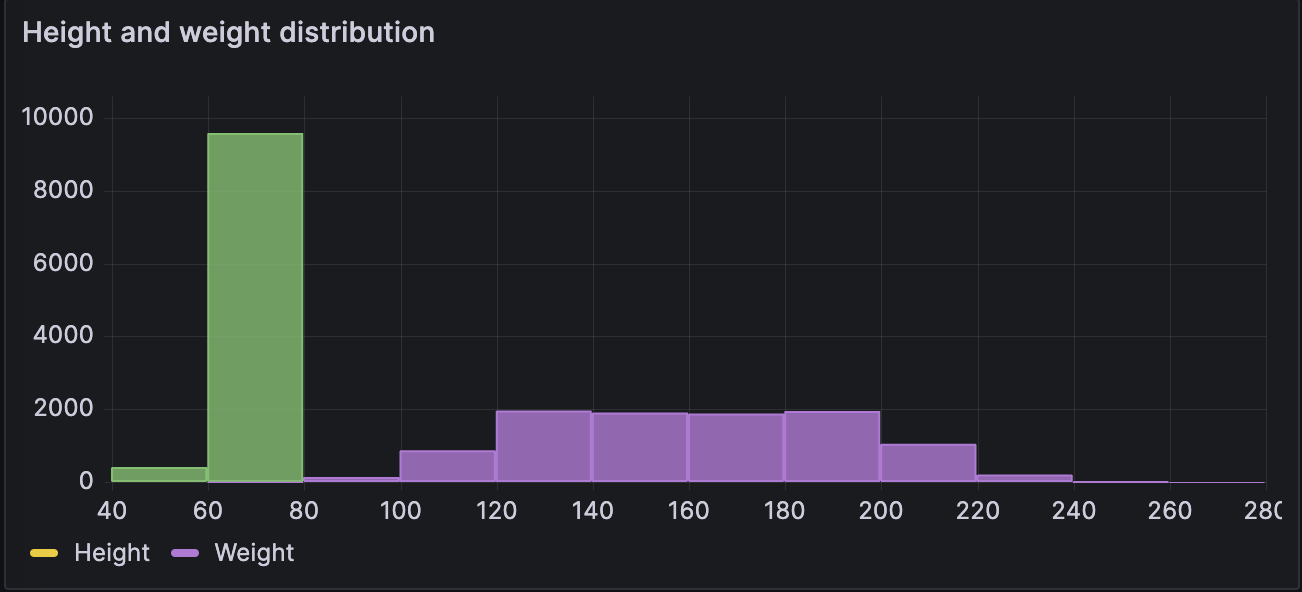
Basic numerical table
| Gender | Height (kg) | Weight (lbs) |
|---|---|---|
| Male | 73.8 | 242 |
| Male | 68.8 | 162 |
| Male | 74.1 | 213 |
| Male | 71.7 | 220 |
| Male | 69.9 | 206 |
| Male | 67.3 | 152 |
| Male | 68.8 | 184 |
The data is converted as follows:
Histogram options
Use the following options to refine your histogram visualization.
Bucket size
The size of the buckets. Leave this empty for automatic bucket sizing (~10% of the full range).
Bucket offset
If the first bucket should not start at zero. A non-zero offset has the effect of shifting the aggregation window. For example, 5-sized buckets that are 0-5, 5-10, 10-15 with a default 0 offset would become 2-7, 7-12, 12-17 with an offset of 2; offsets of 0, 5, or 10, in this case, would effectively do nothing. Typically, this option would be used with an explicitly defined bucket size rather than automatic. For this setting to affect, the offset amount should be greater than 0 and less than the bucket size; values outside this range will have the same effect as values within this range.
Combine series
This will merge all series and fields into a combined histogram.
Line width
Controls line width of the bars.
Fill opacity
Controls the fill opacity bars.
Gradient mode
Set the mode of the gradient fill. Fill gradient is based on the line color. To change the color, use the standard color scheme field option.
Gradient display is influenced by the Fill opacity setting.
None
No gradient fill. This is the default setting.
Opacity
Transparency of the gradient is calculated based on the values on the Y-axis. The opacity of the fill is increasing with the values on the Y-axis.
Hue
Gradient color is generated based on the hue of the line color.
Legend mode
Use these settings to define how the legend appears in your visualization. For more information about the legend, refer to Configure a legend.
- List - Displays the legend as a list. This is a default display mode of the legend.
- Table - Displays the legend as a table.
- Hidden - Hides the legend.
Legend placement
Choose where to display the legend.
- Bottom - Below the graph.
- Right - To the right of the graph.
Legend values
Choose which of the standard calculations to show in the legend. You can have more than one.
Legend calculations
Choose a standard calculations to show in the legend. You can select more than one.



