Presto integration for Grafana Cloud
Presto is an open-source distributed SQL query engine designed for running interactive analytic queries against data sources of all sizes, ranging from gigabytes to petabytes. It allows users to query data where it lives, whether it’s in Hadoop, AWS S3, Cassandra, MySQL, and many other data sources without the need for complex data migration or transformation. The integration with Grafana Cloud enables users to oversee a Presto environment using distinct dashboards. These dashboards display metrics and logs for Presto clusters, workers, coordinators, and logs.
This integration supports Presto 0.28+ running alongisde a JMX exporter 0.19.0+.
This integration includes 7 useful alerts and 4 pre-built dashboards to help monitor and visualize Presto metrics and logs.
Before you begin
In order for the integration to properly work, you must set up the JMX Exporter for Prometheus on each instance in your cluster.
Enable the JMX Exporter
To enable the JMX exporter in Presto you need to add a couple of files within the installation directory. The first file will be called jmx.properties. This file should be created in <presto-installation-directory>/etc/catalog/. The following line should be added into the file:
connector.name=jmx
The second file that needs to be created is jvm.config. The location of this file is typically found/created in <presto-installation-directory>/etc/. The following lines should be appended onto this file. Change the jmxremote.port on the command below for each instance you run, then save the configuration files.
-Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote
-Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.port=<jmx.port>
-Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.ssl=false
-Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.authenticate=false
-javaagent:<path/to/jmx_java_agent.jar>=<exporter_port>:</path/to/jmx_pattern_config.yaml>/config.yamlConfigure the JMX Exporter metrics collection
In order to connect JMX to the Prometheus Exporter, a collector is configured in a config file. This config.yaml file can be placed anywhere and named anything. The contents of this file will be the following:
rules:
- pattern: "com.facebook.presto.execution<name=TaskManager><>(.+): (.*)"
name: "presto_TaskManager_$1"
value: $2
type: UNTYPED
attrNameSnakeCase: false
- pattern: "com.facebook.presto.execution.executor<name=TaskExecutor><>(.+): (.*)"
name: "presto_TaskExecutor_$1"
value: $2
type: UNTYPED
- pattern: "com.facebook.presto.failureDetector<name=HeartbeatFailureDetector><>ActiveCount: (.*)"
name: "presto_HeartbeatDetector_ActiveCount"
value: $1
type: UNTYPED
attrNameSnakeCase: false
- pattern: "com.facebook.presto.metadata<name=DiscoveryNodeManager><>(.+): (.*)"
name: "presto_metadata_DiscoveryNodeManager_$1"
value: $2
type: UNTYPED
attrNameSnakeCase: false
- pattern: "com.facebook.presto.execution<name=QueryManager><>(.+): (.*)"
name: "presto_QueryManager_$1"
value: $2
type: UNTYPED
- pattern: "com.facebook.presto.execution<name=QueryExecution><>(.+): (.*)"
name: "presto_QueryExecution_$1"
value: $2
attrNameSnakeCase: false
- pattern: "com.facebook.presto.memory<name=ClusterMemoryManager><>(.+): (.*)"
name: "presto_ClusterMemoryManager_$1"
value: $2
type: UNTYPED
attrNameSnakeCase: false
- pattern: "com.facebook.presto.memory<type=ClusterMemoryPool, name=(.*)><>(.+): (.*)"
name: "presto_ClusterMemoryPool_$1_$2"
type: UNTYPED
- pattern: "com.facebook.presto.memory<type=MemoryPool, name=(.*)><>(.+): (.*)"
name: "presto_MemoryPool_$1_$2"
type: UNTYPED
- pattern: 'java.lang<name=([^>]+), type=GarbageCollector><LastGcInfo>duration: (\d+)'
name: jvm_gc_duration
value: $2
labels:
name: $1
type: UNTYPED
- pattern: 'java.lang<name=([^>]+), type=GarbageCollector><>CollectionCount: (\d+)'
name: jvm_gc_collection_count
value: $2
labels:
name: $1
type: UNTYPED
- pattern: "java.lang<type=Memory><HeapMemoryUsage>used"
name: jvm_heap_memory_used
type: UNTYPED
- pattern: "java.lang<type=Memory><HeapMemoryUsage>committed"
name: jvm_heap_memory_committed
type: UNTYPED
- pattern: "java.lang<type=Memory><NonHeapMemoryUsage>used"
name: jvm_nonheap_memory_used
type: UNTYPED
- pattern: "java.lang<type=Memory><NonHeapMemoryUsage>committed"
name: jvm_nonheap_memory_committed
type: UNTYPEDValidate the JMX Exporter
The JMX exporter will open a port and report the Prometheus metrics to the exporter port when the Presto instance has been started. To validate that the JMX Exporter is setup correctly, the Prometheus metrics should be available locally via curl:
curl http://localhost:<exporter_port>/metricsConfigure logs location.
By default, Presto does not have a location to store logs. Inside the file located at <presto-installation-directory>/etc/node.properties, the user can configure a location for logs to be placed. The following line configures the log location to be at /var/presto/data/var/log/server.log
node.data-dir=/var/presto/dataInstall Presto integration for Grafana Cloud
- In your Grafana Cloud stack, click Connections in the left-hand menu.
- Find Presto and click its tile to open the integration.
- Review the prerequisites in the Configuration Details tab and set up Grafana Agent to send Presto metrics and logs to your Grafana Cloud instance.
- Click Install to add this integration’s pre-built dashboards and alerts to your Grafana Cloud instance, and you can start monitoring your Presto setup.
Configuration snippets for Grafana Alloy
Advanced mode
The following snippets provide examples to guide you through the configuration process.
To instruct Grafana Alloy to scrape your Presto instances, manually copy and append the snippets to your alloy configuration file, then follow subsequent instructions.
Advanced metrics snippets
prometheus.scrape "metrics_integrations_integrations_presto" {
targets = [{
__address__ = "localhost:<your-instance-port>",
presto_cluster = "<your-presto-cluster-name>",
}]
forward_to = [prometheus.remote_write.metrics_service.receiver]
job_name = "integrations/presto"
}To monitor your Presto instance, you must use a discovery.relabel component to discover your Presto Prometheus endpoint and apply appropriate labels, followed by a prometheus.scrape component to scrape it.
Configure the following properties within each discovery.relabel component:
__address__: The address to your Presto Prometheus metrics endpoint.instancelabel:constants.hostnamesets theinstancelabel to your Grafana Alloy server hostname. If that is not suitable, change it to a value uniquely identifies this Presto instance. Make sure this label value is the same for all telemetry data collected for this instance.presto_clustermust be the value that identifies the Presto cluster this instance belongs to.
If you have multiple Presto servers to scrape, configure one discovery.relabel for each and scrape them by including each under targets within the prometheus.scrape component.
Advanced logs snippets
darwin
local.file_match "logs_integrations_integrations_presto" {
path_targets = [{
__address__ = "localhost",
__path__ = "/var/presto/data/var/log/server.log",
instance = format("%s:<your-instance-port>", constants.hostname),
job = "integrations/presto",
presto_cluster = "<your-presto-cluster-name>",
}]
}
loki.process "logs_integrations_integrations_presto" {
forward_to = [loki.write.grafana_cloud_loki.receiver]
stage.multiline {
firstline = "\\d{4}-\\d{2}-\\d{2}T\\d{2}:\\d{2}:\\d{2}\\.\\d{3}"
max_lines = 0
max_wait_time = "3s"
}
stage.regex {
expression = "\\d{4}-\\d{2}-\\d{2}T\\d{2}:\\d{2}:\\d{2}\\.\\d{3}Z\\s+(?P<level>\\w+)(?P<message>.+)"
}
stage.labels {
values = {
level = null,
}
}
}
loki.source.file "logs_integrations_integrations_presto" {
targets = local.file_match.logs_integrations_integrations_presto.targets
forward_to = [loki.process.logs_integrations_integrations_presto.receiver]
}To monitor your Presto instance logs, you will use a combination of the following components:
local.file_match defines where to find the log file to be scraped. Change the following properties according to your environment:
__address__: The Presto instance address__path__is the Presto logs location. Presto does not have a default log location, but users can configure one within thenode.propertiesfile in their Presto installation directory. Instructions for this integration should lead to it being/var/presto/data/var/log/server.log.instancelabel:constants.hostnamesets theinstancelabel to your Grafana Alloy server hostname. If that is not suitable, change it to a value uniquely identifies this Presto instance. Make sure this label value is the same for all telemetry data collected for this instance.presto_clustermust be the value that identifies the Presto cluster this instance belongs to.
loki.process defines how to process logs before sending it to Loki.
loki.source.file sends logs to Loki.
linux
local.file_match "logs_integrations_integrations_presto" {
path_targets = [{
__address__ = "localhost",
__path__ = "/var/presto/data/var/log/server.log",
instance = format("%s:<your-instance-port>", constants.hostname),
job = "integrations/presto",
presto_cluster = "<your-presto-cluster-name>",
}]
}
loki.process "logs_integrations_integrations_presto" {
forward_to = [loki.write.grafana_cloud_loki.receiver]
stage.multiline {
firstline = "\\d{4}-\\d{2}-\\d{2}T\\d{2}:\\d{2}:\\d{2}\\.\\d{3}"
max_lines = 0
max_wait_time = "3s"
}
stage.regex {
expression = "\\d{4}-\\d{2}-\\d{2}T\\d{2}:\\d{2}:\\d{2}\\.\\d{3}Z\\s+(?P<level>\\w+)(?P<message>.+)"
}
stage.labels {
values = {
level = null,
}
}
}
loki.source.file "logs_integrations_integrations_presto" {
targets = local.file_match.logs_integrations_integrations_presto.targets
forward_to = [loki.process.logs_integrations_integrations_presto.receiver]
}To monitor your Presto instance logs, you will use a combination of the following components:
local.file_match defines where to find the log file to be scraped. Change the following properties according to your environment:
__address__: The Presto instance address__path__is the Presto logs location. Presto does not have a default log location, but users can configure one within thenode.propertiesfile in their Presto installation directory. Instructions for this integration should lead to it being/var/presto/data/var/log/server.log.instancelabel:constants.hostnamesets theinstancelabel to your Grafana Alloy server hostname. If that is not suitable, change it to a value uniquely identifies this Presto instance. Make sure this label value is the same for all telemetry data collected for this instance.presto_clustermust be the value that identifies the Presto cluster this instance belongs to.
loki.process defines how to process logs before sending it to Loki.
loki.source.file sends logs to Loki.
windows
local.file_match "logs_integrations_integrations_presto" {
path_targets = [{
__address__ = "localhost",
__path__ = "/var/presto/data/var/log/server.log",
instance = format("%s:<your-instance-port>", constants.hostname),
job = "integrations/presto",
presto_cluster = "<your-presto-cluster-name>",
}]
}
loki.process "logs_integrations_integrations_presto" {
forward_to = [loki.write.grafana_cloud_loki.receiver]
stage.multiline {
firstline = "\\d{4}-\\d{2}-\\d{2}T\\d{2}:\\d{2}:\\d{2}\\.\\d{3}"
max_lines = 0
max_wait_time = "3s"
}
stage.regex {
expression = "\\d{4}-\\d{2}-\\d{2}T\\d{2}:\\d{2}:\\d{2}\\.\\d{3}Z\\s+(?P<level>\\w+)(?P<message>.+)"
}
stage.labels {
values = {
level = null,
}
}
}
loki.source.file "logs_integrations_integrations_presto" {
targets = local.file_match.logs_integrations_integrations_presto.targets
forward_to = [loki.process.logs_integrations_integrations_presto.receiver]
}To monitor your Presto instance logs, you will use a combination of the following components:
local.file_match defines where to find the log file to be scraped. Change the following properties according to your environment:
__address__: The Presto instance address__path__is the Presto logs location. Presto does not have a default log location, but users can configure one within thenode.propertiesfile in their Presto installation directory. Instructions for this integration should lead to it being/var/presto/data/var/log/server.log.instancelabel:constants.hostnamesets theinstancelabel to your Grafana Alloy server hostname. If that is not suitable, change it to a value uniquely identifies this Presto instance. Make sure this label value is the same for all telemetry data collected for this instance.presto_clustermust be the value that identifies the Presto cluster this instance belongs to.
loki.process defines how to process logs before sending it to Loki.
loki.source.file sends logs to Loki.
Grafana Agent static configuration (deprecated)
The following section shows configuration for running Grafana Agent in static mode which is deprecated. You should use Grafana Alloy for all new deployments.
Before you begin with Grafana Agent static
In order for the integration to properly work, you must set up the JMX Exporter for Prometheus on each instance in your cluster.
Enable the JMX Exporter
To enable the JMX exporter in Presto you need to add a couple of files within the installation directory. The first file will be called jmx.properties. This file should be created in <presto-installation-directory>/etc/catalog/. The following line should be added into the file:
connector.name=jmx
The second file that needs to be created is jvm.config. The location of this file is typically found/created in <presto-installation-directory>/etc/. The following lines should be appended onto this file. Change the jmxremote.port on the command below for each instance you run, then save the configuration files.
-Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote
-Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.port=<jmx.port>
-Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.ssl=false
-Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.authenticate=false
-javaagent:<path/to/jmx_java_agent.jar>=<exporter_port>:</path/to/jmx_pattern_config.yaml>/config.yamlConfigure the JMX Exporter metrics collection
In order to connect JMX to the Prometheus Exporter, a collector is configured in a config file. This config.yaml file can be placed anywhere and named anything. The contents of this file will be the following:
rules:
- pattern: "com.facebook.presto.execution<name=TaskManager><>(.+): (.*)"
name: "presto_TaskManager_$1"
value: $2
type: UNTYPED
attrNameSnakeCase: false
- pattern: "com.facebook.presto.execution.executor<name=TaskExecutor><>(.+): (.*)"
name: "presto_TaskExecutor_$1"
value: $2
type: UNTYPED
- pattern: "com.facebook.presto.failureDetector<name=HeartbeatFailureDetector><>ActiveCount: (.*)"
name: "presto_HeartbeatDetector_ActiveCount"
value: $1
type: UNTYPED
attrNameSnakeCase: false
- pattern: "com.facebook.presto.metadata<name=DiscoveryNodeManager><>(.+): (.*)"
name: "presto_metadata_DiscoveryNodeManager_$1"
value: $2
type: UNTYPED
attrNameSnakeCase: false
- pattern: "com.facebook.presto.execution<name=QueryManager><>(.+): (.*)"
name: "presto_QueryManager_$1"
value: $2
type: UNTYPED
- pattern: "com.facebook.presto.execution<name=QueryExecution><>(.+): (.*)"
name: "presto_QueryExecution_$1"
value: $2
attrNameSnakeCase: false
- pattern: "com.facebook.presto.memory<name=ClusterMemoryManager><>(.+): (.*)"
name: "presto_ClusterMemoryManager_$1"
value: $2
type: UNTYPED
attrNameSnakeCase: false
- pattern: "com.facebook.presto.memory<type=ClusterMemoryPool, name=(.*)><>(.+): (.*)"
name: "presto_ClusterMemoryPool_$1_$2"
type: UNTYPED
- pattern: "com.facebook.presto.memory<type=MemoryPool, name=(.*)><>(.+): (.*)"
name: "presto_MemoryPool_$1_$2"
type: UNTYPED
- pattern: 'java.lang<name=([^>]+), type=GarbageCollector><LastGcInfo>duration: (\d+)'
name: jvm_gc_duration
value: $2
labels:
name: $1
type: UNTYPED
- pattern: 'java.lang<name=([^>]+), type=GarbageCollector><>CollectionCount: (\d+)'
name: jvm_gc_collection_count
value: $2
labels:
name: $1
type: UNTYPED
- pattern: "java.lang<type=Memory><HeapMemoryUsage>used"
name: jvm_heap_memory_used
type: UNTYPED
- pattern: "java.lang<type=Memory><HeapMemoryUsage>committed"
name: jvm_heap_memory_committed
type: UNTYPED
- pattern: "java.lang<type=Memory><NonHeapMemoryUsage>used"
name: jvm_nonheap_memory_used
type: UNTYPED
- pattern: "java.lang<type=Memory><NonHeapMemoryUsage>committed"
name: jvm_nonheap_memory_committed
type: UNTYPEDValidate the JMX Exporter
The JMX exporter will open a port and report the Prometheus metrics to the exporter port when the Presto instance has been started. To validate that the JMX Exporter is setup correctly, the Prometheus metrics should be available locally via curl:
curl http://localhost:<exporter_port>/metricsConfigure logs location.
By default, Presto does not have a location to store logs. Inside the file located at <presto-installation-directory>/etc/node.properties, the user can configure a location for logs to be placed. The following line configures the log location to be at /var/presto/data/var/log/server.log
node.data-dir=/var/presto/dataInstall Presto integration
- In your Grafana Cloud stack, click Connections in the left-hand menu.
- Find Presto and click its tile to open the integration.
- Review the prerequisites in the Configuration Details tab and set up Grafana Agent to send Presto metrics and logs to your Grafana Cloud instance.
- Click Install to add this integration’s pre-built dashboards and alerts to your Grafana Cloud instance, and you can start monitoring your Presto setup.
Post-install configuration for the Presto integration
After enabling the metrics generation, instruct the Grafana Agent to scrape the Presto metrics that have been created by the JMX exporter. The Grafana Agent config is stored in the default location for each respective operating system. More documentation for the Grafana Agent can be found here: Grafana Agent documentation.
Enable the integration by adding the suggested snippets to your agent configuration file.
If you want to show logs and metrics signals correlated in your dashboards as a single pane of glass, ensure the following:
jobandinstancelabel values must match for the Presto integration and logs scrape config in your agent configuration file.jobmust be set tointegrations/presto(already configured in the snippets).instancemust be set to a value that uniquely identifies your Presto instance.presto_clustermust be the value that identifies the Presto cluster this instance belongs to.__path__is the Presto logs location. Presto does not have a default log location, but users can configure one within thenode.propertiesfile in their Presto installation directory. Instructions for this integration should lead to the__path__being/var/presto/data/var/log/server.log. Make sure to changetargetsin the snippet according to your host name andJMX_EXPORTER_PORT.
Configuration snippets for Grafana Agent
Below metrics.configs.scrape_configs, insert the following lines and change the URLs according to your environment:
- job_name: integrations/presto
metrics_path: /metrics
static_configs:
- targets: ["<your-instance-hostname>:<your-instance-port>"]
labels:
presto_cluster: '<your-presto-cluster-name>'Below logs.configs.scrape_configs, insert the following lines according to your environment.
- job_name: integrations/presto
static_configs:
- targets: [localhost]
labels:
job: integrations/presto
presto_cluster: '<your-presto-cluster-name>'
instance: '<your-instance-hostname>:<your-instance-port>'
__path__: /var/presto/data/var/log/server.log
pipeline_stages:
- multiline:
firstline: '\d{4}-\d{2}-\d{2}T\d{2}:\d{2}:\d{2}\.\d{3}'
- regex:
expression: '\d{4}-\d{2}-\d{2}T\d{2}:\d{2}:\d{2}\.\d{3}Z\s+(?P<level>\w+)(?P<message>.+)'
- labels:
level:Full example configuration for Grafana Agent
Refer to the following Grafana Agent configuration for a complete example that contains all the snippets used for the Presto integration. This example also includes metrics that are sent to monitor your Grafana Agent instance.
integrations:
prometheus_remote_write:
- basic_auth:
password: <your_prom_pass>
username: <your_prom_user>
url: <your_prom_url>
agent:
enabled: true
relabel_configs:
- action: replace
source_labels:
- agent_hostname
target_label: instance
- action: replace
target_label: job
replacement: "integrations/agent-check"
metric_relabel_configs:
- action: keep
regex: (prometheus_target_sync_length_seconds_sum|prometheus_target_scrapes_.*|prometheus_target_interval.*|prometheus_sd_discovered_targets|agent_build.*|agent_wal_samples_appended_total|process_start_time_seconds)
source_labels:
- __name__
# Add here any snippet that belongs to the `integrations` section.
# For a correct indentation, paste snippets copied from Grafana Cloud at the beginning of the line.
logs:
configs:
- clients:
- basic_auth:
password: <your_loki_pass>
username: <your_loki_user>
url: <your_loki_url>
name: integrations
positions:
filename: /tmp/positions.yaml
scrape_configs:
# Add here any snippet that belongs to the `logs.configs.scrape_configs` section.
# For a correct indentation, paste snippets copied from Grafana Cloud at the beginning of the line.
- job_name: integrations/presto
static_configs:
- targets: [localhost]
labels:
job: integrations/presto
presto_cluster: '<your-presto-cluster-name>'
instance: '<your-instance-hostname>:<your-instance-port>'
__path__: /var/presto/data/var/log/server.log
pipeline_stages:
- multiline:
firstline: '\d{4}-\d{2}-\d{2}T\d{2}:\d{2}:\d{2}\.\d{3}'
- regex:
expression: '\d{4}-\d{2}-\d{2}T\d{2}:\d{2}:\d{2}\.\d{3}Z\s+(?P<level>\w+)(?P<message>.+)'
- labels:
level:
metrics:
configs:
- name: integrations
remote_write:
- basic_auth:
password: <your_prom_pass>
username: <your_prom_user>
url: <your_prom_url>
scrape_configs:
# Add here any snippet that belongs to the `metrics.configs.scrape_configs` section.
# For a correct indentation, paste snippets copied from Grafana Cloud at the beginning of the line.
- job_name: integrations/presto
metrics_path: /metrics
static_configs:
- targets: ["<your-instance-hostname>:<your-instance-port>"]
labels:
presto_cluster: '<your-presto-cluster-name>'
global:
scrape_interval: 60s
wal_directory: /tmp/grafana-agent-walDashboards
The Presto integration installs the following dashboards in your Grafana Cloud instance to help monitor your system.
- Presto coordinator
- Presto logs overview
- Presto overview
- Presto worker
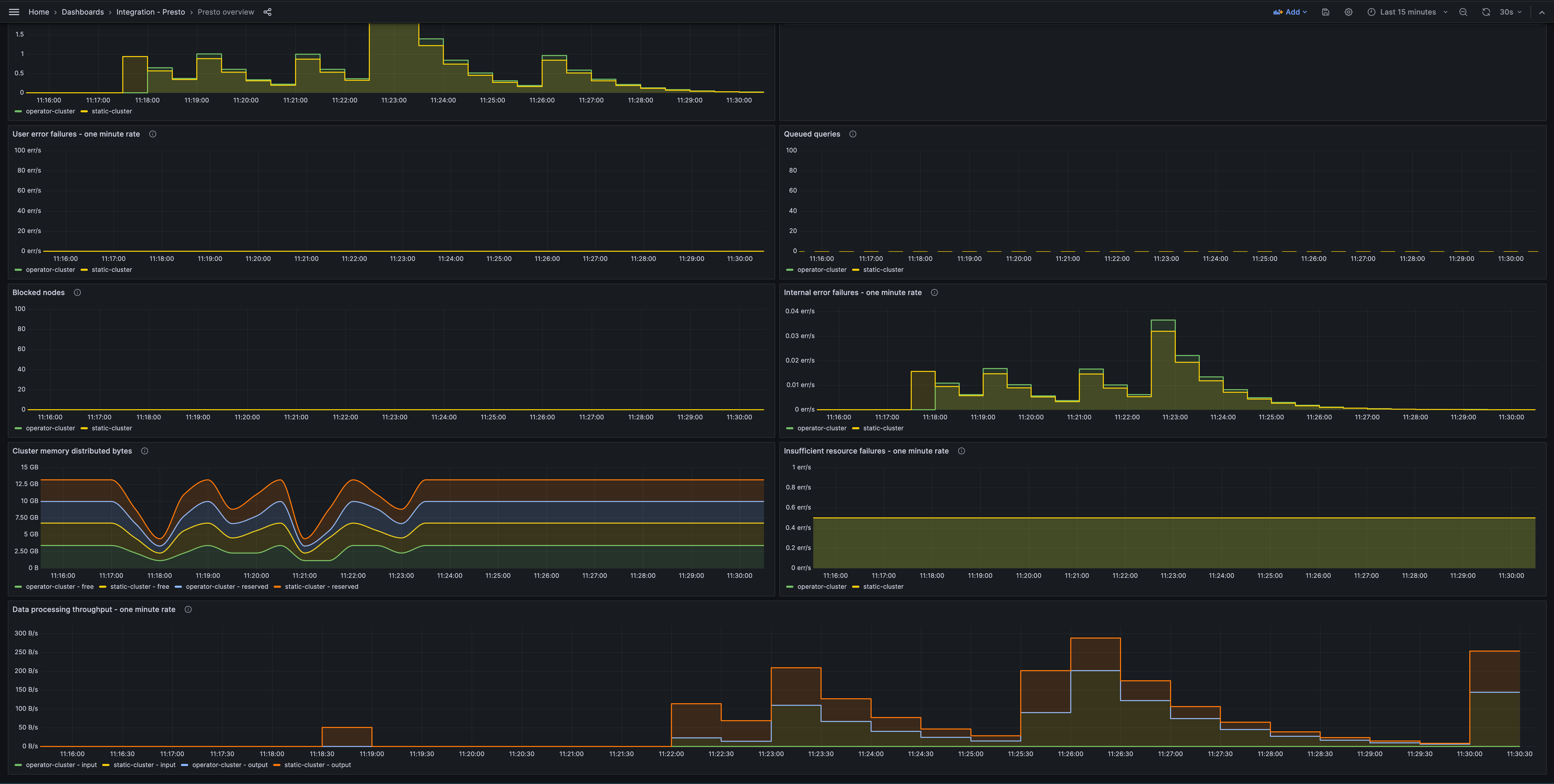
Presto overview (queries)

Presto overview (processing)
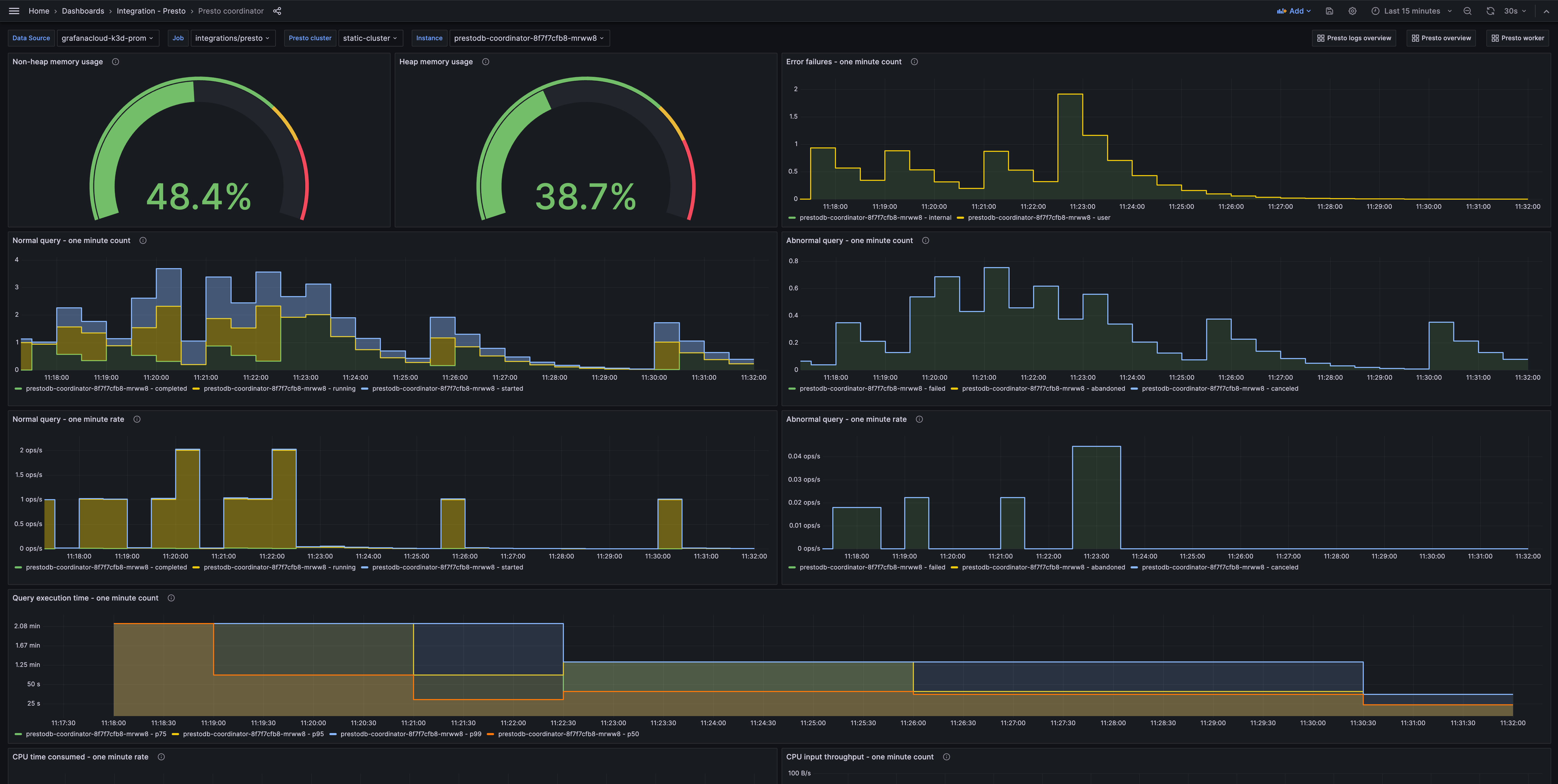
Presto coordinator (queries)
Alerts
The Presto integration includes the following useful alerts:
| Alert | Description |
|---|---|
| PrestoHighInsufficientResources | Critical: The amount of failures that are occurring due to insufficient resources are scaling, causing saturation in the system. |
| PrestoHighTaskFailuresWarning | Warning: The amount of tasks that are failing is increasing, this might affect query processing and could result in incomplete or incorrect results. |
| PrestoHighTaskFailuresCritical | Critical: The amount of tasks that are failing has reached a critical level. This might affect query processing and could result in incomplete or incorrect results. |
| PrestoHighQueuedTaskCount | Warning: The amount of tasks that are being put in queue is increasing. A high number of queued tasks can lead to increased query latencies and degraded system performance. |
| PrestoHighBlockedNodes | Critical: The amount of nodes that are blocked due to memory restrictions is increasing. Blocked nodes can cause performance degradation and resource starvation. |
| PrestoHighFailedQueriesWarning | Warning: The amount of queries failing is increasing. Failed queries can prevent users from accessing data, disrupt analytics processes, and might indicate underlying issues with the system or data. |
| PrestoHighFailedQueriesCritical | Critical: The amount of queries failing has increased to critical levels. Failed queries can prevent users from accessing data, disrupt analytics processes, and might indicate underlying issues with the system or data. |
Metrics
The most important metrics provided by the Presto integration, which are used on the pre-built dashboards and Prometheus alerts, are as follows:
- jvm_gc_collection_count
- jvm_gc_duration
- jvm_heap_memory_committed
- jvm_heap_memory_used
- jvm_nonheap_memory_committed
- jvm_nonheap_memory_used
- presto_ClusterMemoryPool_general_BlockedNodes
- presto_ClusterMemoryPool_general_FreeDistributedBytes
- presto_ClusterMemoryPool_reserved_FreeDistributedBytes
- presto_HeartbeatDetector_ActiveCount
- presto_MemoryPool_general_FreeBytes
- presto_MemoryPool_reserved_FreeBytes
- presto_QueryExecution_Executor_QueuedTaskCount
- presto_QueryManager_AbandonedQueries_OneMinute_Count
- presto_QueryManager_AbandonedQueries_TotalCount
- presto_QueryManager_CanceledQueries_OneMinute_Count
- presto_QueryManager_CanceledQueries_TotalCount
- presto_QueryManager_CompletedQueries_OneMinute_Count
- presto_QueryManager_CompletedQueries_OneMinute_Rate
- presto_QueryManager_ConsumedCpuTimeSecs_OneMinute_Count
- presto_QueryManager_CpuInputByteRate_OneMinute_Total
- presto_QueryManager_ExecutionTime_OneMinute_P50
- presto_QueryManager_ExecutionTime_OneMinute_P75
- presto_QueryManager_ExecutionTime_OneMinute_P95
- presto_QueryManager_ExecutionTime_OneMinute_P99
- presto_QueryManager_FailedQueries_OneMinute_Count
- presto_QueryManager_FailedQueries_TotalCount
- presto_QueryManager_InsufficientResourcesFailures_OneMinute_Rate
- presto_QueryManager_InsufficientResourcesFailures_TotalCount
- presto_QueryManager_InternalFailures_OneMinute_Count
- presto_QueryManager_InternalFailures_OneMinute_Rate
- presto_QueryManager_QueuedQueries
- presto_QueryManager_RunningQueries
- presto_QueryManager_StartedQueries_OneMinute_Count
- presto_QueryManager_StartedQueries_OneMinute_Rate
- presto_QueryManager_UserErrorFailures_OneMinute_Count
- presto_QueryManager_UserErrorFailures_OneMinute_Rate
- presto_TaskExecutor_ProcessorExecutor_CompletedTaskCount
- presto_TaskExecutor_ProcessorExecutor_CorePoolSize
- presto_TaskExecutor_ProcessorExecutor_PoolSize
- presto_TaskExecutor_ProcessorExecutor_QueuedTaskCount
- presto_TaskManager_FailedTasks_TotalCount
- presto_TaskManager_InputDataSize_OneMinute_Rate
- presto_TaskManager_OutputDataSize_OneMinute_Rate
- presto_TaskManager_OutputPositions_OneMinute_Rate
- presto_TaskManager_TaskNotificationExecutor_PoolSize
- presto_metadata_DiscoveryNodeManager_ActiveCoordinatorCount
- presto_metadata_DiscoveryNodeManager_ActiveNodeCount
- presto_metadata_DiscoveryNodeManager_ActiveResourceManagerCount
- presto_metadata_DiscoveryNodeManager_InactiveNodeCount
- up
Changelog
# 1.0.1 - November 2024
- Update status panel check queries
# 1.0.0 - November 2023
- Initial releaseCost
By connecting your Presto instance to Grafana Cloud, you might incur charges. To view information on the number of active series that your Grafana Cloud account uses for metrics included in each Cloud tier, see Active series and dpm usage and Cloud tier pricing.



