Docker integration for Grafana Cloud
Docker is a popular open-source platform that enables developers to create, deploy, and run applications in a virtualized environment called a container. It allows developers to package an application with all its dependencies, libraries, and other components required to run it, into a single container image. The Docker integration collects metrics and logs from a Docker instance and provides useful pre-built dashboards to monitor them.
This integration includes 2 pre-built dashboards to help monitor and visualize Docker metrics and logs.
Before you begin
This integration uses Grafana Alloy Docker service discovery feature to identify and collect logs. To do this, it must have access to docker daemon. To give this access, add the “alloy” user to “docker” group with the following command:
sudo usermod -a -G docker alloyElevated privileges are required to run cAdvisor in Grafana Alloy in standalone mode, See cAdvisor documentation. After installing Grafana Alloy, you must give it elevated permissions. Follow the instructions below:
Open the systemctl unit file to change the user running Grafana Alloy process:
sudo systemctl edit --full alloy.serviceChange User=alloy to User=root and save the file.
Reload systemctl changes using:
sudo systemctl daemon-reloadThen restart Grafana Alloy:
sudo systemctl restart alloy.serviceIn order to successfully collect logs and test the integration connection, at least one container should be running in the docker engine.
Install Docker integration for Grafana Cloud
- In your Grafana Cloud stack, click Connections in the left-hand menu.
- Find Docker and click its tile to open the integration.
- Review the prerequisites in the Configuration Details tab and set up Grafana Agent to send Docker metrics and logs to your Grafana Cloud instance.
- Click Install to add this integration’s pre-built dashboards to your Grafana Cloud instance, and you can start monitoring your Docker setup.
Configuration snippets for Grafana Alloy
Simple mode
These snippets are configured to scrape a single Docker engine running locally with default ports.
Manually copy and append the following snippets into your Grafana Alloy configuration file.
Integrations snippets
prometheus.exporter.cadvisor "integrations_cadvisor" {
docker_only = true
}
discovery.relabel "integrations_cadvisor" {
targets = prometheus.exporter.cadvisor.integrations_cadvisor.targets
rule {
target_label = "job"
replacement = "integrations/docker"
}
rule {
target_label = "instance"
replacement = constants.hostname
}
}
prometheus.scrape "integrations_cadvisor" {
targets = discovery.relabel.integrations_cadvisor.output
forward_to = [prometheus.remote_write.metrics_service.receiver]
}Logs snippets
linux
discovery.docker "logs_integrations_docker" {
host = "unix:///var/run/docker.sock"
refresh_interval = "5s"
}
discovery.relabel "logs_integrations_docker" {
targets = []
rule {
target_label = "job"
replacement = "integrations/docker"
}
rule {
target_label = "instance"
replacement = constants.hostname
}
rule {
source_labels = ["__meta_docker_container_name"]
regex = "/(.*)"
target_label = "container"
}
rule {
source_labels = ["__meta_docker_container_log_stream"]
target_label = "stream"
}
}
loki.source.docker "logs_integrations_docker" {
host = "unix:///var/run/docker.sock"
targets = discovery.docker.logs_integrations_docker.targets
forward_to = [loki.write.grafana_cloud_loki.receiver]
relabel_rules = discovery.relabel.logs_integrations_docker.rules
refresh_interval = "5s"
}Advanced mode
To instruct Grafana Alloy to scrape your docker engine, go though the subsequent instructions.
The snippets provide examples to guide you through the configuration process.
First, manually copy and append the following snippets into your Grafana Alloy configuration file.
Then follow the instructions below to modify the necessary variables.
Advanced integrations snippets
prometheus.exporter.cadvisor "integrations_cadvisor" {
docker_only = true
}
discovery.relabel "integrations_cadvisor" {
targets = prometheus.exporter.cadvisor.integrations_cadvisor.targets
rule {
target_label = "job"
replacement = "integrations/docker"
}
rule {
target_label = "instance"
replacement = constants.hostname
}
}
prometheus.scrape "integrations_cadvisor" {
targets = discovery.relabel.integrations_cadvisor.output
forward_to = [prometheus.remote_write.metrics_service.receiver]
}Add a pair of prometheus.exporter.cadvisor and discovery.relabel to your Grafana Alloy configuration to monitor a docker daemon.
For ease of use, the provided snippets sets the instance label to the hostname using the constants.hostname Agent Flow constant variable.
If you want to monitor more than one daemon running within the same host, set a different value for each to avoid instance label conflicts.
You will also need to set the docker_host and containerd_host properties within prometheus.exporter.cadvisor for each daemon.
There is an array of options available within this component, like setting up tls connection, specific cgroup collection, amongst others.
Refer to prometheus.exporter.cadvisor in Grafana Alloy reference documentation for a complete description of the configuration options.
Finally, reference each discovery.relabel component within the targets property of the prometheus.scrape component.
Advanced logs snippets
linux
discovery.docker "logs_integrations_docker" {
host = "unix:///var/run/docker.sock"
refresh_interval = "5s"
}
discovery.relabel "logs_integrations_docker" {
targets = []
rule {
target_label = "job"
replacement = "integrations/docker"
}
rule {
target_label = "instance"
replacement = constants.hostname
}
rule {
source_labels = ["__meta_docker_container_name"]
regex = "/(.*)"
target_label = "container"
}
rule {
source_labels = ["__meta_docker_container_log_stream"]
target_label = "stream"
}
}
loki.source.docker "logs_integrations_docker" {
host = "unix:///var/run/docker.sock"
targets = discovery.docker.logs_integrations_docker.targets
forward_to = [loki.write.grafana_cloud_loki.receiver]
relabel_rules = discovery.relabel.logs_integrations_docker.rules
refresh_interval = "5s"
}Add a group of discovery.docker, discovery.relabel and loki.source.docker to your Grafana Alloy configuration to monitor a docker daemon.
For ease of use, the provided snippets sets the instance label to the hostname using the constants.hostname Agent Flow constant variable.
If you want to monitor more than one daemon running within the same host, set a different value for each to avoid instance label conflicts.
You will also need to set the host property within discovery.docker and loki.source.docker for each daemon.
Make sure that for each docker daemon you are monitoring the instance label is set to the same value within the discovery.relabel components collecting cadvisor metrics and the daemon logs.
Grafana Agent static configuration (deprecated)
The following section shows configuration for running Grafana Agent in static mode which is deprecated. You should use Grafana Alloy for all new deployments.
Before you begin
The integration collects Docker container metrics through embedded cAdvisor in Grafana agent. This integration is only suited for Linux docker engine. For Windows & Mac, the Docker Desktop for Grafana Cloud can be used.
This integration uses the Docker service discovery feature of the Grafana agent to identify and collect logs. In order for the integration to work, the Grafana agent must have access to docker daemon. To give the agent access to docker daemon, you need to add the “grafana-agent” user to “docker” group with the following command:
sudo usermod -a -G docker grafana-agentElevated privileges are required to run cAdvisor in Grafana agent in standalone mode, See cAdvisor documentation. After installing the Grafana agent, you can give the agent elevated permissions by changing the user of the Grafana agent installed service by editing the systemctl unit file:
sudo systemctl edit --full grafana-agent.serviceChange User=grafana-agent to User=root and save the file. Then reload systemctl changes using:
sudo systemctl daemon-reloadThen restart the Grafana agent:
sudo systemctl restart grafana-agent.serviceIn order to successfully collect logs and test the integration connection, at least one container should be running in the docker engine.
Install Docker integration for Grafana Cloud
- In your Grafana Cloud stack, click Connections in the left-hand menu.
- Find Docker and click its tile to open the integration.
- Review the prerequisites in the Configuration Details tab and set up Grafana Agent to send Docker metrics and logs to your Grafana Cloud instance.
- Click Install to add this integration’s pre-built dashboards to your Grafana Cloud instance, and you can start monitoring your Docker setup.
Post-install configuration for the Docker integration
This integration is configured to work with the cadvisor exporter, which is embedded in Grafana Agent.
Enable the integration by adding the provided snippet to your agent configuration file.
This integration supports metrics and logs for Docker containers. If you want to see your logs and metrics correlated on your dashboards, as a single pane of glass, ensure the following:
jobandinstancelabel values must match forcadvisorintegration andlogsscrape config in your agent configuration file.joblabel must be set tointegrations/docker(already configured in the snippets through relabel_configs).instancelabel must be set to a value that uniquely identifies your Docker Node. Replace it according to your environment (instanceentry forcadvisorintegration and the second relabel_config forlogsscrape). Note that if you uselocalhostfor multiple nodes, the dashboards will not be able to filter correctly by instance.
The log snippet is configured to collect logs from Docker using Docker service discovery.
For a full description of configuration options see how to configure the cadvisor_config block in the agent documentation.
Configuration snippets for Grafana Agent
Below integrations, insert the following lines and change the URLs according to your environment:
cadvisor:
enabled: true
docker_only: true
instance: '<your-instance-name>' # must match instance used in logs
relabel_configs:
- action: replace
replacement: integrations/docker
target_label: jobBelow logs.configs.scrape_configs, insert the following lines according to your environment.
- job_name: integrations/docker
docker_sd_configs:
- host: unix:///var/run/docker.sock
refresh_interval: 5s
relabel_configs:
- action: replace
replacement: integrations/docker
target_label: job
- action: replace
replacement: '<your-instance-name>' # must match instance used in cadvisor
target_label: instance
- source_labels:
- __meta_docker_container_name
regex: '/(.*)'
target_label: container
- source_labels:
- __meta_docker_container_log_stream
target_label: streamFull example configuration for Grafana Agent
Refer to the following Grafana Agent configuration for a complete example that contains all the snippets used for the Docker integration. This example also includes metrics that are sent to monitor your Grafana Agent instance.
integrations:
prometheus_remote_write:
- basic_auth:
password: <your_prom_pass>
username: <your_prom_user>
url: <your_prom_url>
agent:
enabled: true
relabel_configs:
- action: replace
source_labels:
- agent_hostname
target_label: instance
- action: replace
target_label: job
replacement: "integrations/agent-check"
metric_relabel_configs:
- action: keep
regex: (prometheus_target_sync_length_seconds_sum|prometheus_target_scrapes_.*|prometheus_target_interval.*|prometheus_sd_discovered_targets|agent_build.*|agent_wal_samples_appended_total|process_start_time_seconds)
source_labels:
- __name__
# Add here any snippet that belongs to the `integrations` section.
# For a correct indentation, paste snippets copied from Grafana Cloud at the beginning of the line.
cadvisor:
enabled: true
docker_only: true
instance: '<your-instance-name>' # must match instance used in logs
relabel_configs:
- action: replace
replacement: integrations/docker
target_label: job
logs:
configs:
- clients:
- basic_auth:
password: <your_loki_pass>
username: <your_loki_user>
url: <your_loki_url>
name: integrations
positions:
filename: /tmp/positions.yaml
scrape_configs:
# Add here any snippet that belongs to the `logs.configs.scrape_configs` section.
# For a correct indentation, paste snippets copied from Grafana Cloud at the beginning of the line.
- job_name: integrations/docker
docker_sd_configs:
- host: unix:///var/run/docker.sock
refresh_interval: 5s
relabel_configs:
- action: replace
replacement: integrations/docker
target_label: job
- action: replace
replacement: '<your-instance-name>' # must match instance used in cadvisor
target_label: instance
- source_labels:
- __meta_docker_container_name
regex: '/(.*)'
target_label: container
- source_labels:
- __meta_docker_container_log_stream
target_label: stream
metrics:
configs:
- name: integrations
remote_write:
- basic_auth:
password: <your_prom_pass>
username: <your_prom_user>
url: <your_prom_url>
scrape_configs:
# Add here any snippet that belongs to the `metrics.configs.scrape_configs` section.
# For a correct indentation, paste snippets copied from Grafana Cloud at the beginning of the line.
global:
scrape_interval: 60s
wal_directory: /tmp/grafana-agent-walDashboards
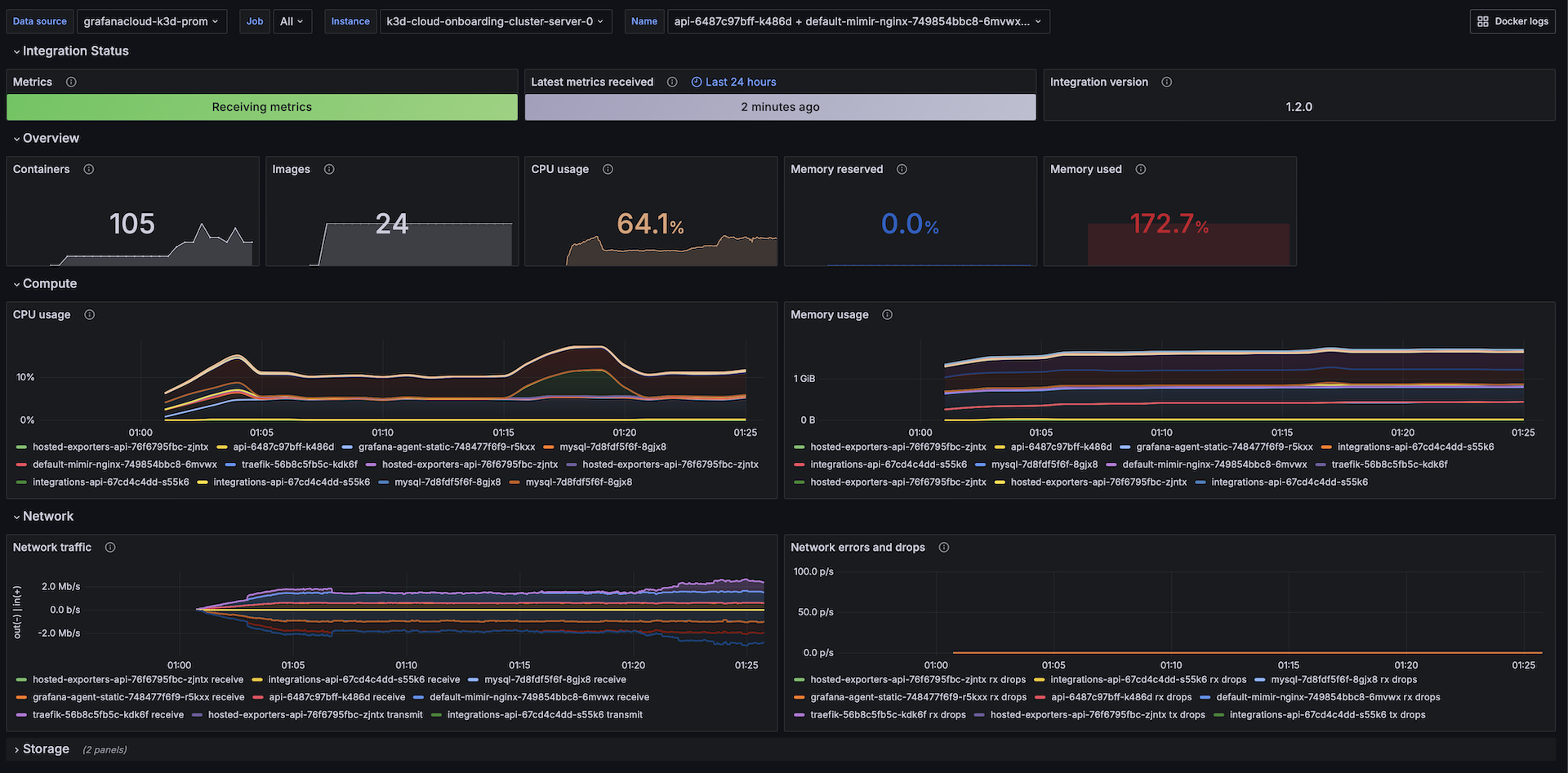
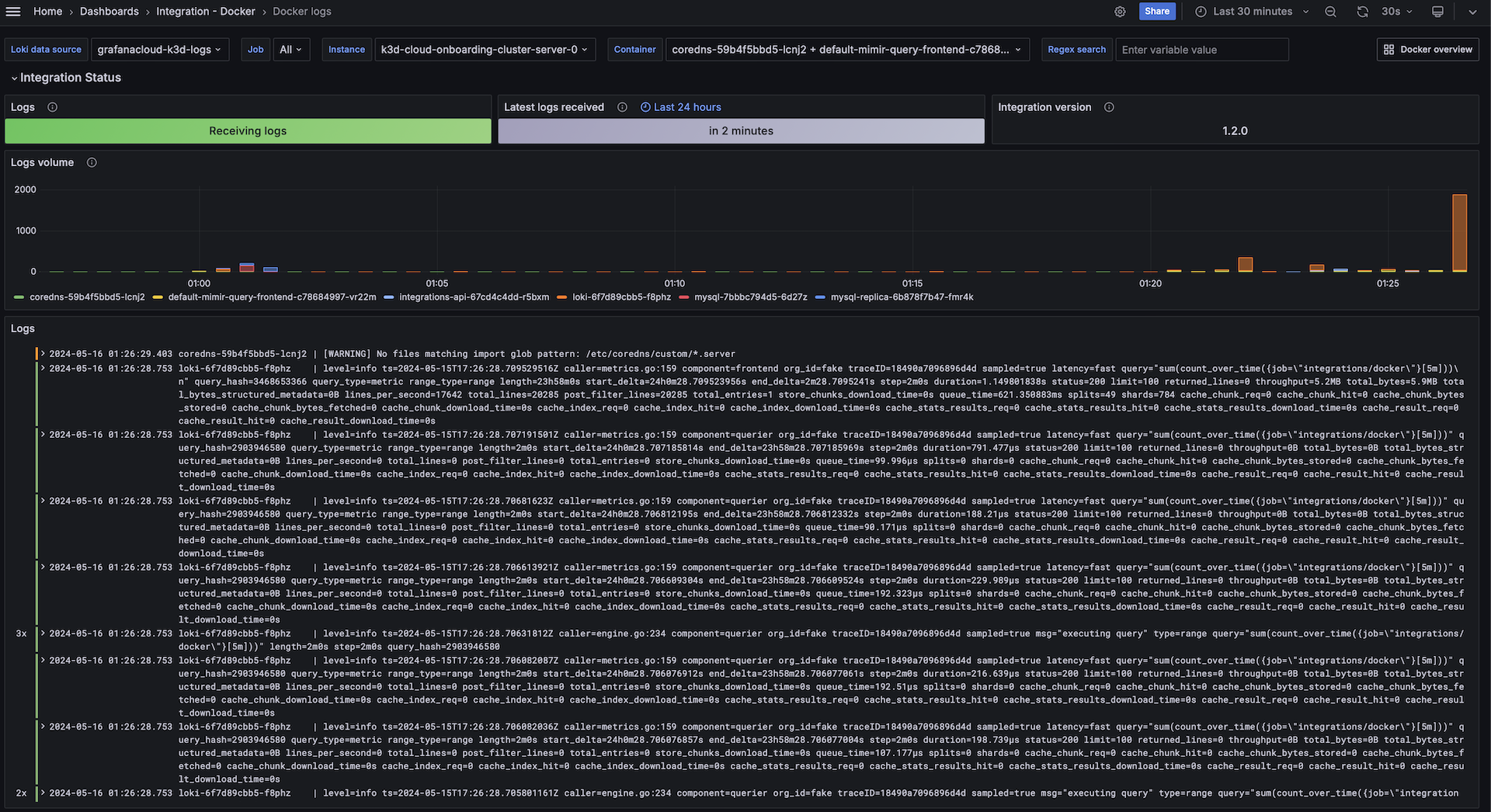
The Docker integration installs the following dashboards in your Grafana Cloud instance to help monitor your system.
- Docker logs
- Docker overview
Overview & Compute
Logs
Metrics
The most important metrics provided by the Docker integration, which are used on the pre-built dashboards, are as follows:
- container_cpu_usage_seconds_total
- container_fs_reads_total
- container_fs_usage_bytes
- container_fs_writes_total
- container_last_seen
- container_memory_usage_bytes
- container_network_receive_bytes_total
- container_network_receive_errors_total
- container_network_receive_packets_dropped_total
- container_network_transmit_bytes_total
- container_network_transmit_errors_total
- container_network_transmit_packets_dropped_total
- container_spec_memory_reservation_limit_bytes
- machine_memory_bytes
- machine_scrape_error
- up
Changelog
# 1.3.3 - November 2024
- Update status panel check queries
# 1.3.2 - September 2024
* Mixin update:
- Split DiskIO metric into reads/writes metrics
- Legend improvements:
- Add {{device}} to all disks signals
- Add {{interface}} to all network signals
- fix softmax=100 on CPU panel.
# 1.3.1 - August 2024
* Update mixin
* Add filter for root cgroup metrics
# 1.3.0 - July 2024
* Add asserts support
# 1.2.1 - June 2024
* Update pre instructions
# 1.2.0 - May 2024
* Mixin update:
- Reworked panels based on commonlib
- Added storage metrics
- Added network errors/drops metrics
- Updated logs dashboard
# 1.1.0 - January 2024
* Remove windows and darwin as supported platforms
- For windows and darwin, the recommended integration to use now is docker-desktop
# 1.0.0 - January 2024
* Update mixin to remove deprecated angular panels
# 0.1.0 - September 2023
* Add updated status panels
# 0.0.8 - August 2023
* Add regex filter for logs datasource
# 0.0.7 - August 2023
* New Filter Metrics option for configuring the Grafana Agent, which saves on metrics cost by dropping any metric not used by this integration. Beware that anything custom built using metrics that are not on the snippet will stop working.
* New hostname relabel option, which applies the instance name you write on the text box to the Grafana Agent configuration snippets, making it easier and less error prone to configure this mandatory label.
# 0.0.6 - April 2023
* Add missing descriptions to panels
# 0.0.5 - November 2022
* Add integration status panel
# 0.0.4 - May 2022
* Update mixin to latest version:
- Fix log line counts
# 0.0.3 - April 2022
* Add instructions for scraping docker logs
* Update integration to work with embedded Grafana agent Cadvisor
# 0.0.2 - April 2022
* Update mixin to latest version:
- Update variable display names
- Rename datasource to prometheus_datasource
- Group by instance as well on disk usage
- Fix total images / containers showing up as double
- Add integration status panels
- Convert to gridpos
- Remove deprecated singlestat panel
- Disable shared tooltip
# 0.0.1 - October 2020
* Initial releaseCost
By connecting your Docker instance to Grafana Cloud, you might incur charges. To view information on the number of active series that your Grafana Cloud account uses for metrics included in each Cloud tier, see Active series and dpm usage and Cloud tier pricing.



