
Open source at Grafana Labs in 2023: Year in review
At Grafana Labs, open source has always been part of our DNA. But in 2023 — a year in which we reflected on 10 years of Grafana, among other major OSS milestones — the power of our open source community felt especially palpable.
“The success of Grafana has really been driven by the efforts of everyone who’s joined us on our mission — not just the Grafana Labs team, but the wider community,” said Grafana Labs Co-founder Anthony Woods during the GrafanaCON 2023 keynote in June. “You’ve been our teachers, our testers, our troubleshooters, and, of course, our spell checkers. And I’m really excited about the future. We are really just getting started with Grafana.”
Woods’ remarks came just before the unveiling of Grafana 10, the latest major release of the open source visualization software that, over the last decade, has grown to have more than 20 million users around the world. (BTW, want to learn more about the origin story of Grafana and how our OSS community has evolved? Check out our new documentary, “The Story of Grafana.”)
From significant updates to the LGTM Stack to the launch of new OSS projects like Grafana Pyroscope and Grafana Beyla, 2023 was a blockbuster year for open source software and the OSS community here at Grafana Labs.
Here are some of the highlights.
Grafana LGTM Stack updates
Grafana Loki
This year, Grafana Loki — the horizontally scalable, highly available, multi-tenant log aggregation system inspired by Prometheus — celebrated its fifth anniversary. And there sure was a lot to celebrate.

In September, the Grafana Loki GitHub repository hit 20,000 stars, an achievement that underscored the momentum behind the open source project. And today, there are more than 100,000 active Loki clusters.
Several big updates were also made to Loki throughout the year, including:
- Enhanced log ingestion and OpenTelemetry support via structured metadata.
- Graduating our new TSDB index to General Availability with the Loki 2.8 release. Directly inspired by the Prometheus TSDB storage format, Loki’s TSDB index offers improved resource utilization and more performant querying.
- Several LogQL enhancements that accelerate line parsing and regex parsing.
For more information, check out our recent Loki blog posts and Loki documentation.
Grafana
A major release, a 10th anniversary, a documentary chronicling its rise — there were a lot of big moments for Grafana in 2023.
With the release of Grafana 10, the OSS project evolved significantly to offer a more intuitive user experience, more robust security and authentication capabilities, and, of course, innovative new ways to visualize and derive value from data. Some notable Grafana 10 updates include:
- Grafana Scenes: A new frontend library that allows Grafana plugin developers to build dynamic, dashboard-like experiences directly into their app plugins.
- Grafana public dashboards: Share dashboards with anyone outside your org, plus let users collapse rows, hide queries, and zoom into panels.
- More data visualization options: A new trend panel for graphing ascending numeric X-axis data, and a new datagrid panel that streamlines data management via a spreadsheet-like interface.
- Grafana subfolders: A new feature that allows you to organize dashboards into folders based on business units, teams, or whatever other structure you prefer.
- SAML authentication: A new guided setup experience that streamlines the SAML configuration process.
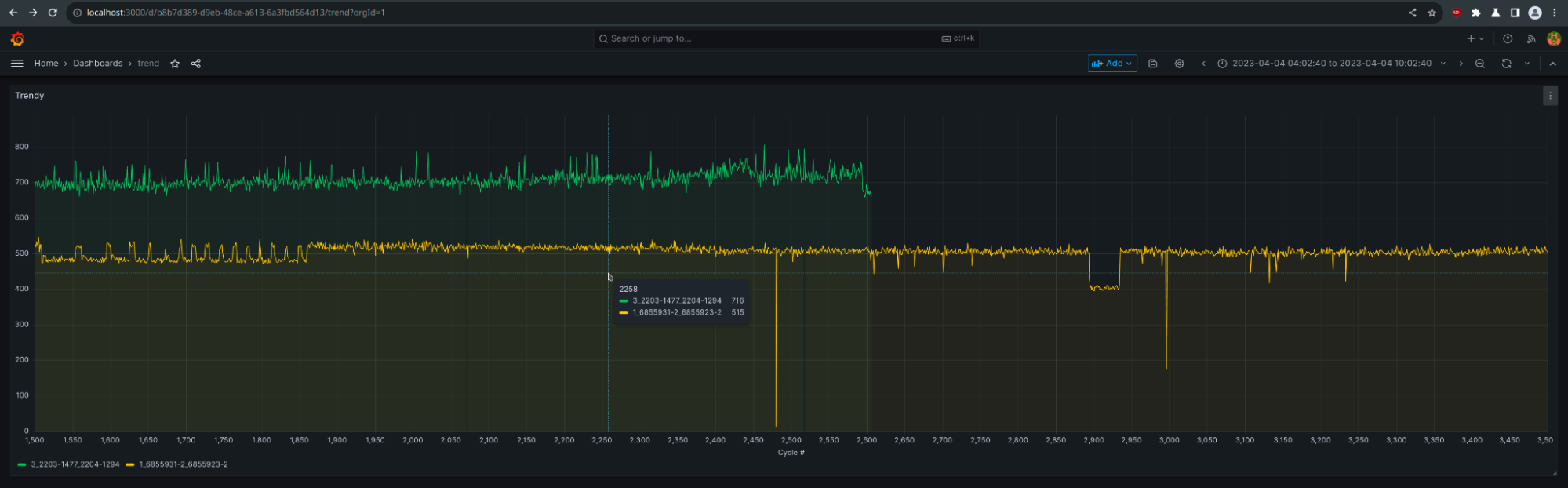
These new Grafana 10 features (and many more) were exciting for another reason: they were unveiled just as the Grafana community celebrated, and looked back on, 10 years of the open source visualization tool.
As Grafana Labs Co-founder and CEO Raj Dutt put it during the GrafanaCON 2023 keynote: “It’s hard to believe it’s been 10 years since Torkel [Ödegaard] launched Grafana, growing from a small man with a big dream to becoming the most popular data visualization software in the world.”
To learn more, read our most recent Grafana blog posts and our Grafana documentation.
Grafana Tempo
This year, the OSS community also welcomed the latest major release of Grafana Tempo, the open source, easy-to-use, and highly scalable distributed tracing backend.
The Tempo 2.0 release introduced two important new features:
- Support for TraceQL: Inspired by PromQL and LogQL, TraceQL is a new query language designed specifically for discovering traces. With TraceQL, Tempo users can find the exact trace they’re looking for easier and faster than ever.
- The Apache Parquet trace storage backend: As the new default backend for Tempo, Apache Parquet stores trace data in an entirely open format, enabling users to tap into the large ecosystem of databases and querying engines that support Parquet.
Several other incremental releases of Tempo, including 2.1, 2.2, and 2.3, throughout the year made these new features even more powerful and performant.
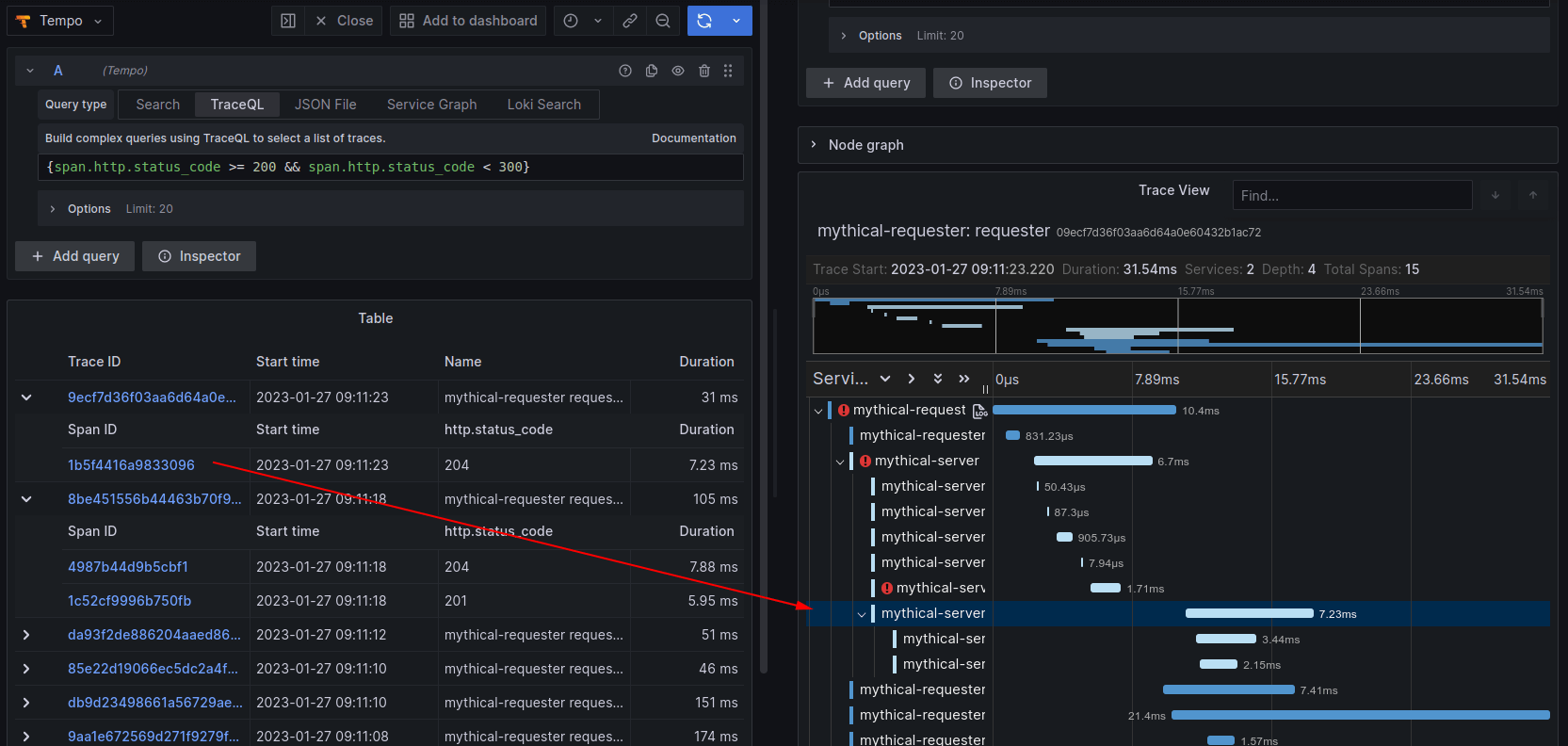
Learn more about the latest updates to Tempo in our recent Grafana Tempo blog posts and Tempo documentation.
Grafana Mimir
Since launching Mimir — the open source, highly available, multi-tenant TSDB for long-term storage — we made a number of enhancements to increase scale, make it easier to get started, and boost query performance. And in 2023, we continued to push the envelope, in terms of making Mimir the most scalable and performant open source time series database in the world.
Some of the latest Mimir updates include:
- A series of improvements that enable Mimir to run any query with bounded memory utilization.
- Leveraging the structure of the Prometheus TSDB to avoid some inverted index lookups and reduce store-gateway memory usage in some clusters by up to 64%.
- Dropping mmap from the store-gateway to further improve query performance.
- New metrics for tracking native histograms in active series.
With roughly 3,000 stars (and counting) on GitHub, Mimir continues to grow in popularity — and we can’t wait to see what the future holds.
To learn more about Grafana Mimir, check out our free webinar “Intro to Grafana Mimir: The open source time series database that scales to 1 billion metrics & beyond” and our Grafana Mimir documentation.
Celebrating our OSS community with the Grafana Champions Program
Another milestone in the Grafana Labs open source community this year was the launch of our Grafana Champions program.
The new program, introduced in August, aims to recognize experts within the Grafana community, amplify their contributions, and help them foster a collaborative partnership with the Grafana Labs team.
Grafana Champions hold a variety of roles and perform a variety of job functions, but they all have a habit of giving back to the community — whether it’s by writing a blog post, presenting at a conference, or contributing code — and helping others.
Check out our Champions page to see the Grafana experts currently in the program. And if you’re interested in joining, we encourage you to apply today!
More open source projects
In addition to the LGTM Stack, we made a series of updates to other OSS projects this year, including Grafana k6, our load testing and reliability tool; Grafana Agent, our vendor-neutral telemetry collector; Grafana Faro, our highly configurable web SDK for real user monitoring (RUM); and Grafana OnCall, our on-call management system.
We also launched two new open source projects: Grafana Pyroscope and Grafana Beyla.
Grafana Pyroscope
What do you get when you combine Grafana Phlare (the open source continuous profiling tool we announced in 2022) with the powerful continuous profiling technology we gained through our acquisition of Pyroscope? Grafana Pyroscope, a highly efficient and scalable open source profiling database.
Launched in August, Grafana Pyroscope 1.0 offers developers greater visibility into their code’s resource usage — which, in turn, helps them better understand application performance and optimize spend. Here are a few important features to know:
- Horizontal scalability: You can run Grafana Pyroscope across multiple machines, making it easy to scale the database to handle profiling volumes.
- High availability: Grafana Pyroscope replicates incoming profiles, mitigating the risk of data loss — even in the event of a failure.
- Cost-effective profile storage: Grafana Pyroscope’s use of object storage for long-term data storage helps cut costs.
- Natively multi-tenant: You can isolate data and queries, making it possible for different teams or business units to share the same database.

Check out our Pyroscope documentation and the GrafanaCON 2023 on-demand session “Continuous profiling with Grafana Pyroscope: developer experience, flame graphs, and more” to learn more.
Grafana Beyla
At ObservabilityCON 2023, we announced the general availability of Grafana Beyla 1.0.
Grana Beyla is an open source eBPF auto-instrumentation tool for OpenTelemetry and Prometheus applications. It helps you quickly get started with application observability for Go, C/C++, Rust, Python, Ruby, Java, NodeJS, .NET, and more. With the release of Beyla 1.0, we launched two new features that weren’t part of the Beyla public preview:
- Multi-process support: In the public preview of Grafana Beyla, you needed to deploy a separate Beyla instance as a “sidecar” for each application you were instrumenting, which could sometimes lead to unnecessary resource consumption. With the multi-process support in Beyla 1.0, we addressed this challenge; you can now configure a single Beyla instance to monitor a variety of apps.
- Heuristic HTTP path decorator: This new routes decorator automatically turns high cardinality URL paths into low cardinality routes to reduce costs — without the need for extensive configuration.
Other Beyla improvements are already on our radar, including distributed tracing and the ability to monitor other protocols beyond HTTP and gRPC.
For more information, refer to our Beyla documentation.
OpenTelemetry and Prometheus
Grafana Labs has always been an active member of the OpenTelemetry and Prometheus communities. In fact, we are the only company leading in contributions to both open source projects.
We have been supporting OTLP as the primary input protocol for Grafana Tempo since its inception, and Grafana Agent embeds parts of the OpenTelemetry Collector. And we continue to increase our investment in the OTel open source project, whether it’s by incorporating OpenTelemetry into our Application Observability strategy in Grafana Cloud or supporting Prometheus native histograms in the OTel Collector. Interoperability between OpenTelemetry and Prometheus has also been a main area of focus.
This year, we introduced new OpenTelemetry components for Grafana Agent Flow. We also remained active and engaged within the community; at KubeCon + CloudNativeCon North America 2023, Juraci Paixão Kröhling, Principal Software Engineer at Grafana Labs, joined fellow OpenTelemetry project maintainers in leading an OTel “Contribfest,” a session that encouraged attendees to help fix bugs and add new features to the OSS project. Also at KubeCon, Grafana Labs Engineering Director Ryan Perry led a talk about our experiences and efforts in integrating continuous profiling into OpenTelemetry.
We look forward to continued collaboration and innovation within both the Prometheus and OTel communities.
For more information, check out our OpenTelemetry and Prometheus documentation.
We want to hear from you about your observability practice! Fill out our short and easy observability survey. All responses will be kept anonymous, and you’ll be helping the community get a better understanding of the state of observability.



