
How to connect and monitor your Raspberry Pi with Grafana Cloud
The Raspberry Pi is a popular and inexpensive device that comes in many shapes and forms. It’s a popular hobbyist tool that is generally purchased to run all kinds of software experiments on. But make no mistake, even though a Raspberry Pi comes in a tiny form factor, it’s a fully functional computer! And as a result of its low cost and small size, the Raspberry Pi is a very powerful and efficient device with a tiny footprint, which makes it the perfect candidate to run an always-live monitoring experiment on.
What’s your favorite flavor of Pi?
Getting a working Raspberry Pi is fairly straightforward: you start by purchasing any of the available hardware and then you get to install an operating system of your choice. And when it comes to the operating system, there are a wealth of options. You could go with the officially supported Raspberry Pi OS or opt for a different one altogether, such as any other compatible Linux distribution. A common alternative is Ubuntu for Raspberry Pi, among others.
In this article we’ll assume you have a Raspberry Pi and have it set up to run a Linux operating system. From there, we will connect your Raspberry Pi to a free Grafana Cloud account to collect and visualize system metrics. Grafana Cloud is the easiest way to start observing metrics, logs, traces, and create dashboards. When you sign up for a Grafana Cloud account, you get all the following for free, forever:
- 10,000 series for Prometheus or Graphite metrics
- 50GB of logs
- 500VUh of k6 testing
- 14-day retention for metrics and logs
- Synthetic monitoring
- Access for up to 3 team members
Included with your account is a 14-day free trial of Grafana Cloud Pro, which comes with additional storage limits, alongside a host of premium features with team collaboration in mind, like longer data retention, advanced authentication, reporting, and usage insights. After the 14 days are up, you can decide if you’d like to pay and continue using the upgraded Pro plan or be automatically converted to the free plan, which is still pretty amazing.
Let’s get started.
Sign up for Grafana Cloud
To sign up for a Grafana Cloud account:
- Navigate to https://grafana.com/products/cloud/
- Click Start for free on the banner.
- Follow the instructions to finish setting up your account and access the Cloud Portal.
Configure a pre-built dashboard
Grafana Cloud comes with a library of pre-built dashboards, sets of metrics, and groups of alerts that are bundled together in the form of integrations, to make monitoring a variety of systems and services easier.
To install the Linux Server integration, which will allow Grafana Cloud to receive metrics sent from your Raspberry Pi:
- Log in to Grafana.com to enter the Cloud Portal and click Log In in the Grafana box (if you are doing this at a later time than when you signed up for your account).

- The first time you log in to Grafana from the Cloud Portal you are automatically taken to the Walkthrough.
- If this is not your first time, hover over the Integrations logo (it looks like a lightning bolt) in the left column and click Walkthrough.

- You will see a list of available Integrations. Select Linux Server then scroll down to the bottom of the list and click Next step.

- In order to install the Linux integration, you must first install and configure the Grafana Agent on your Raspberry Pi. Click Other Distribution under Choose your OS, and follow the instructions you are provided. These will also help you generate the agent config file.
Note: For the Raspberry Pi, you may need to replace amd64 in any commands where it appears with armv6, armv7, or arm64 depending on which Raspberry Pi you are using and whether you are using a 32-bit or 64-bit operating system. Generally the 64-bit can use amd64. See this wikipedia page for a list of Raspberry Pi hardware versions and which Arm architecture each uses.
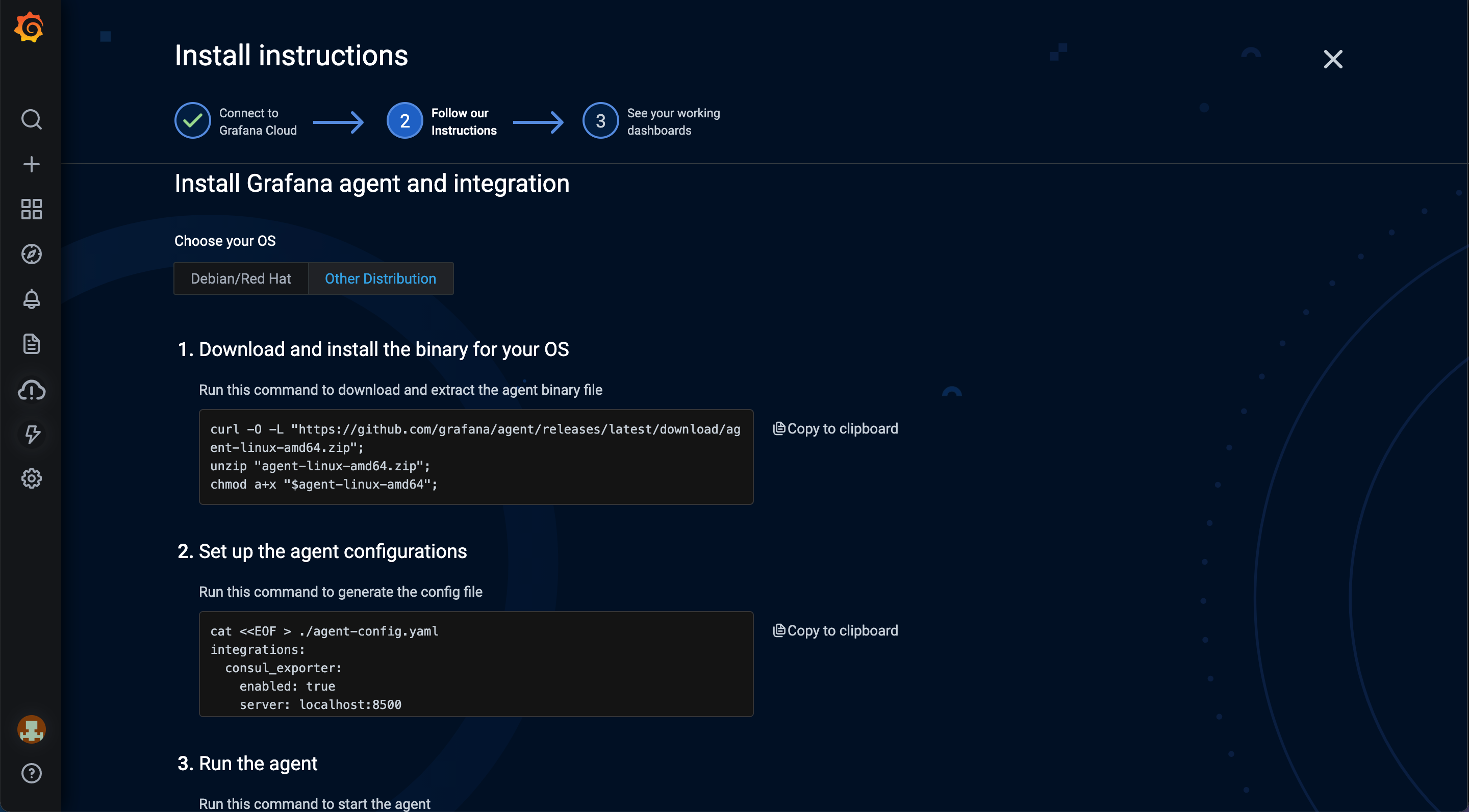
- The final command you enter will start the agent running on your Raspberry Pi.
- When you are done installing the agent and it is running, click Check Connection to confirm the agent is properly sending metrics to Grafana Cloud. Later, after you get everything up and running, you may want to make the agent run as a service, so you don’t have to start it from the command line every time your system boots up.
- If metrics are being received, you will receive a notification. Click Next.

- Click See the dashboard to view the list of your dashboards.

- The Linux server dashboard is called Nodes. Click it to open the dashboard.
Summary
The flexibility of the Raspberry Pi is what makes it so appealing for tinkering with a home project. When it comes to monitoring it, the result is the same: There are so many options out there. But the plethora of available choices and configurations can no doubt make the task daunting, especially if your end goal isn’t to monitor your Raspberry Pi itself but instead leveraging it for another task, like building a sourdough starter monitoring system.
So while using the agent and integrations with Grafana Cloud isn’t the only method for monitoring your Raspberry Pi, especially if you’re already pretty familiar with the Grafana and Prometheus ecosystem, it’s definitely an easier and faster process than rolling your own stack, as shown in this alternate guide. For example, if you wanted to monitor your machine without the agent and Linux integration, you would have to:
- Find the appropriate Prometheus release for your operating system.
- Install and configure Prometheus yourself.
- Find the appropriate exporter for your machine and operating system.
- Install and update your Prometheus configuration.
- Set up Prometheus remote_write to connect to Grafana Cloud manually.
- Create the dashboard and visualizations to query from your data source.
In short, when you install the Grafana Agent and Linux node integration with Grafana Cloud, the configurations, metric collection, metric push, and dashboards are done for you, and we’re constantly trying to improve the process to make it even simpler. That leaves more time for you to focus on all of the cool ideas you have in store for your Raspberry Pi!



